Diagnósticos diferenciais
comuns
Upper airway cough syndrome (UACS; postnasal drip)
História
frequent throat clearing, postnasal drip, nasal discharge, nasal obstruction or sneezing typical, halitosis
Exame físico
mucopurulent secretions in the nasopharynx and oropharynx or cobblestone appearance of posterior oropharynx
Primeira investigação
- therapeutic trial:
response to empiric therapy with antihistamine and decongestant
Mais
Outras investigações
Asthma
História
wheezing, chest tightness, dyspnea, symptom variability, strong family history of asthma/atopic disease, cough, paroxysms, exacerbation by irritants or seasonal exposures; cough may sometimes be the principal or sole symptom, usually worse at night (cough-variant asthma)
Exame físico
wheezing and prolonged expiratory phase on pulmonary exam
Primeira investigação
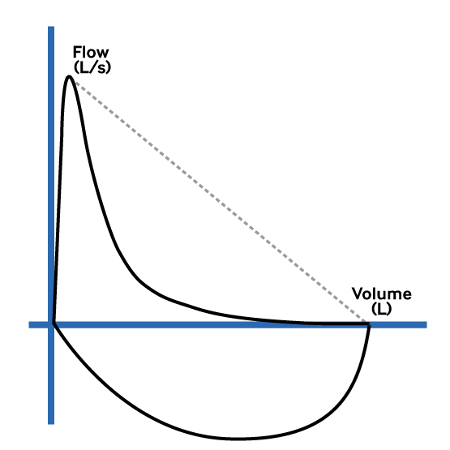
- spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio and bronchodilator reversibility [BDR] test):
FEV1/forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio: below the lower limit of normal (LLN; if available) or <70% (if LLN not available) is positive for airflow obstruction; BDR test: improvement in FEV1 of 12% or more in response to beta agonists (or to a treatment trial with corticosteroids), together with an increase in volume of 200 mL or more is positive for reversibility of airway obstruction
Mais - peak expiratory flow (PEF):
may be reduced; may be variability (>10%) of measurements recorded at different times of the day
More
Other investigations
- fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO):
elevated (>40 parts per billion)
More - other noninvasive airway inflammation biomarkers (blood and sputum eosinophil counts and eosinophilic cationic protein):
elevated
- therapeutic trial:
improvement in symptoms following a 2-4 week course of an inhaled corticosteroid or a leukotriene receptor antagonist
- bronchoprovocation testing:
provocative concentration of methacholine causing a 20% fall in FEV1 (PC20) <4 mg/mL
More - CBC:
normal or elevated eosinophils and/or neutrophilia
- serum IgE antibodies:
elevated antigen-specific IgE antibodies
More - skin-prick allergy testing:
may be positive for allergen
More
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
History
heartburn, dysphagia, acid regurgitation, association of cough with slouched posture, phonation, rising from bed, or eating suggest reflux disease; may be silent
Exam
no differentiating features on exam, may be overweight or obese
1st investigation
- therapeutic trial of proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs):
relief of symptoms
More
Nonasthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis (NAEB)
Chronic bronchitis/COPD
History
history of smoking may be present; cough may produce sputum; dyspnea, especially exertional, may accompany the cough
Exam
mild cases: most respiratory exams are normal, may show quiet breath sounds, prolonged expiratory phase, rhonchi, or wheezes; advanced cases: cyanosis, barrel chest, use of accessory muscles of inspiration, increased S2 over left sternal border, or peripheral edema
1st investigation
- spirometry:
reduced FEV1 and forced vital capacity (FVC); postbronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70 (airflow limitation)
More
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor)
History
dry cough, typically associated with tickling or scratching sensation in the throat; cough may begin within days or months of initiating ACE inhibitor therapy
Exam
no specific exam findings
1st investigation
- stop ACE inhibitor use:
resolution of cough
More
Other investigations
Pneumonia
History
fever, malaise, cough, usually productive of sputum, chest pain
Exam
dullness to percussion, decreased breath sounds, and presence of rales
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
infiltrate suggestive of pneumonia
Other investigations
- WBC (blood):
usually elevated but nonspecific
- serum C-reactive protein (CRP):
may be elevated
More - sputum Gram stain and culture:
presence of microorganisms and leukocytes in a good sputum sample (<25 squamous epithelial cells per field) supports the diagnosis of respiratory tract infection
Postinfectious cough
History
cough of duration between 3 and 8 weeks following symptoms of acute respiratory infection; nasal/sinus congestion, nonpurulent nasal discharge, sore throat
Exam
diagnosis is clinical and one of exclusion
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
normal, rules out pneumonia
Other investigations
- WBC (blood):
usually elevated but nonspecific
- sputum Gram stain and culture:
presence of microorganisms and leukocytes in a good sputum sample (<25 squamous epithelial cells per field) supports the diagnosis of respiratory tract infection
Bordetella pertussis infection
History
paroxysms of cough, post-tussive vomiting, or inspiratory whooping sound; more likely if local epidemiology suggests increased prevalence
Exam
petechiae and conjunctival hemorrhages may result from cough paroxysms; lung examination is typically normal
1st investigation
- nasopharyngeal culture (if symptoms <2 weeks):
positive
More
Other investigations
- polymerase chain reaction, and/or serology (if symptoms present >4 weeks):
positive
Uncommon
Lung cancer
History
history of tobacco smoking, change in character of chronic cough, hemoptysis, hoarseness, chest pain, weight loss, superior vena cava syndrome (localized edema of face and upper extremities, facial plethora, distended neck and chest veins), symptoms related to distant metastases and advanced stages of cancer
Exam
central lung cancers may cause unilateral localized wheezing; superior vena cava syndrome; cachexia and symptoms related to distant metastases (e.g., bone pain) are late symptoms
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
presence of the lesion
More
Other investigations
- CT chest:
presence of the lesion and locoregional disease
- sputum cytology:
may document presence of malignant cells
- bronchoscopy:
presence of tumor
More
Bronchiectasis and chronic suppurative lung disease
History
cough productive of large amounts of mucopurulent sputum, diurnal variation (e.g., worse in the morning), positional worsening; dyspnea, wheezing, hemoptysis; paroxysmal cough nonproductive of sputum may sometimes be present
Exam
crackles and wheezing, predominantly over lower lobes; clubbing in a minority of patients
1st investigation
Other investigations
- pulmonary function tests:
irreversible obstructive defect, with FEV1/forced vital capacity (FVC) <70%
More
Interstitial lung disease
History
dyspnea of subacute onset dominates the clinical picture; cough typically dry
Exam
dry, velcro crackles, typically over lung bases; clubbing may be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
- pulmonary function tests:
restrictive pattern with total lung capacity <80%, functional residual capacity <80%, and vital capacity <80%, with diffusion capacity for CO <80%
More - biopsy:
pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia
Sarcoidosis
History
most patients asymptomatic; symptomatic patients: shortness of breath, dyspnea on exertion, and chest pain are present in minority of patients; low-grade fever; other symptoms reflect involvement of various organs
Exam
most often normal; skin lesions (erythema nodosum and maculopapular skin lesions), enlargement of lacrimal glands, lymphadenopathy in cervical, supraclavicular, or axillary areas; redness of eye, tearing, and photophobia may represent uveitis
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
various findings, bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, reticular infiltrates; fibrosis with decreased lung volumes in late sarcoidosis
More
Other investigations
- chest CT with high-resolution cuts:
bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, interstitial infiltrates
- pulmonary function tests:
often normal, but may show nonspecific reduction in diffusion capacity, obstruction, restriction, or mixed picture
More - bronchoscopy with biopsy:
noncaseating granuloma is supportive, but other granulomatous disorders should be reasonably excluded with special stains and clinical assessment
More
Tuberculosis (TB)
History
residence in/visit to high-prevalence area; immunosuppressed status (e.g., HIV infection, immunosuppressant medication, transplant recipients, diabetes, dialysis treatment); epidemiological risk factors, particularly close contact with active TB; history of anorexia, malaise, weight loss, fever, or night sweats; chronic cough productive of sputum, occasionally associated with hemoptysis
Exam
fever, cachexia, tachycardia; asymmetry in chest movement and dullness to percussion due to pleural effusion, bronchial breathing, crackles, rales due to an infiltrate or rhonchi in presence of significant bronchial purulence; palpable extrathoracic lymphadenopathy is uncommon
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
may demonstrate atelectasis from airway compression, pleural effusion, consolidation, pulmonary infiltrates, mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, upper zone fibrosis
More - sputum acid-fast bacilli smear and culture:
presence of acid-fast bacilli (Ziehl-Neelsen stain) in specimen
More - nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT):
positive for M tuberculosis
More
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage:
positive for acid-fast bacilli
More - lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan (LF-LAM) assay:
positive
More - contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography scan:
primary TB: mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis with central node attenuation and peripheral enhancement, delineated cavities; postprimary TB: centrilobular nodules and tree-in-bud pattern
More
Recurrent aspiration
History
dysphagia, association of cough with eating/drinking, fear of choking with eating/drinking; may have history of neurologic disease including stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease
Exam
signs of neurologic disease such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
persistent lower lobe infiltrates
- swallow evaluation:
aspiration
More
Other investigations
Zenker diverticulum
History
dysphagia present in the majority of patients; regurgitation of bland undigested food; frequent aspiration; noisy deglutition (gurgling); halitosis; voice changes
Exam
halitosis, voice changes
1st investigation
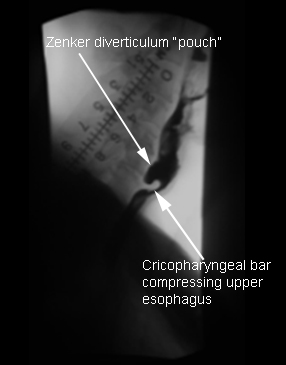
- barium esophagram:
positive contrast within the structure connected to the posterior wall of esophagus is consistent with a diverticulum
More
Other investigations
- endoscopy:
visualization of diverticulum
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA)
History
most patients have no symptoms attributable to TAA at the time of diagnosis; most common initial symptom is vague pain, which can occur in the chest, back, flank, or abdomen; hoarseness due to stretching or compression of left recurrent laryngeal nerve; tracheal deviation, persistent cough, or other respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain; dysphagia (uncommon) due to compression of the esophagus by the aneurysm; sudden and catastrophic hemoptysis or hematemesis; neurologic deficits including paraplegia
Exam
generally no obvious physical findings in chest area unless tracheal deviation is present; patients with an abdominal component may have a pulsatile abdominal mass similar to pure abdominal aortic aneurysms; signs of arterial perfusion differentials in both upper and lower extremities; evidence of visceral ischemia; focal neurologic deficits; murmur of aortic regurgitation; bruits
1st investigation
- chest radiograph:
widened mediastinum, prominence of the aortic knob, or tracheal deviation
Other investigations
- spiral CT of chest with three-dimensional reconstructions:
visualization of aneurysm, seen as an increase in size of a section of the aorta
- MRI and magnetic resonance angiography:
visualization of aneurysm, seen as an increase in size of a section of the aorta
Foreign body
History
abrupt onset, more common in young children
Exam
may be asymptomatic or show signs of airways obstruction, including cough, wheeze, decreased breath sounds, dyspnea, or fever
1st investigation
- laryngoscopy/bronchoscopy:
visualization of foreign body
- chest x-ray:
visualization of foreign body (if object is radiopaque)
Other investigations
- chest CT:
visualization of foreign body
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
History
occupational/environmental exposure to allergens (e.g., farmers, bird breeders), progressive dyspnea, fatigue, and weight loss
Exam
clubbing, increased respiratory rate, inspiratory crackles over lower lung fields
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
fibrotic changes; loss of lung volume particularly affecting the upper lobes
Other investigations
- chest CT:
features of fibrosis
- IgG testing:
high titers with antigen-specific antibodies
Bronchiolitis
History
age <1 year, cough, wheeze, and dyspnea, history of prematurity, underlying cardiopulmonary disease or immunodeficiency
Exam
high respiratory rate, accessory muscle use, retractions, wheezes, crackles, purulent secretions on bronchoscopy
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
consolidation and atelectasis in severe disease
Other investigations
- virology:
may be positive for respiratory syncytial virus
More - high-resolution CT scan:
signs of small airways disease
Tropical filarial pulmonary eosinophilia
History
Travel to endemic area (sub-Saharan Africa, Indian subcontinent, southeast Asia, Oceania); dry, paroxysmal cough, frequently nocturnal
Exam
frequently normal; wheezing, rhonchi, crackles may be present on lung exam; some patients develop hepatosplenomegaly
1st investigation
- blood count with differential:
eosinophilia
- chest x-ray:
increased interstitial markings
Other investigations
- filarial antibody levels:
elevated
- serum IgE:
elevated
Cough hypersensitivity syndrome (somatic cough, psychogenic cough, unexplained chronic cough, refractory chronic cough)
History
extensive evaluation has ruled out other causes; patients may report an urge to cough triggered by itch, scratchy throat, tickle or globus sensation; cough improves following behavior modification
Exam
usually unremarkable
1st investigation
- none:
extensive evaluation has already ruled out other causes
More
Other investigations
Obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS)
History
snoring, diurnal somnolence, agitation and sweating at night, headache, morning xerostomia (dry mouth) and sore throat, depressed mood, irritability, loss of libido; total score of ≥11 on Epworth sleepiness scale supports the diagnosis
Exam
elevated BP, obesity, nasal obstruction, macroglossia, tonsillar hypertrophy, obstruction by the palate, low soft palate, retrognathism, micrognathia
1st investigation
Other investigations
- fiber optic endoscopy:
may see nasal polyps or tumors, or hypertrophic lingual tonsils
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer