Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- dysuria (in women)
- lymphadenopathy
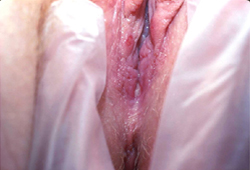
- genital ulcer
- oral ulcer
- fever
Other diagnostic factors
- tingling sensation
- headache/aseptic meningitis
Risk factors
- HIV infection (risk factor for clinical disease)
- use of immunosuppressive medications (risk factor for clinical disease)
- female sex (risk factor for seropositivity)
- black race (risk factor for seropositivity)
- increasing age (risk factor for seropositivity)
- high-risk sexual behavior (risk factor for seropositivity)
- lack of condom use (risk factor for seropositivity)
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- HSV polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- viral culture
Tests to consider
- Glycoprotein G-based type-specific serology (gG1 and gG2)
Treatment algorithm
CNS involvement: encephalitis or meningitis
disseminated visceral involvement: esophagitis, pneumonitis, or hepatitis
genital disease: first episode, immunocompetent, nonpregnant
genital disease: first episode, immunocompromised, nonpregnant
genital disease: recurrent episode, immunocompetent, nonpregnant
genital disease: recurrent episode, immunocompromised, nonpregnant
genital disease: primary or first-episode, pregnant
genital disease: recurrent episode, pregnant
oral disease: first episode, immunocompetent
oral disease: first episode, immunocompromised
oral disease: recurrent episode, immunocompetent
oral disease: recurrent episode, immunocompromised
genital disease: sexually active or frequent severe recurrences, immunocompetent, nonpregnant
genital disease: sexually active or frequent severe recurrences, immunocompromised, nonpregnant
genital disease: pregnant
oral disease: frequent severe recurrences, immunocompetent
oral disease: frequent severe recurrences, immunocompromised
Contributors
Authors
Benjamin D. Lorenz, MD
Assistant Professor
Division of Hospital Medicine
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital
Washington
DC
Disclosures
BDL declares that he has no competing interests. Since completing the 2024 review, BDL has become an employee of Moderna and has resigned as a contributor.
Acknowledgements
Dr Benjamin D. Lorenz would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Christine Johnson and Dr Anna Wald, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
CJ reports funding from AiCuris; grants from Agenus, Gilead, Genocea, Sanofi, and Vical to conduct clinical research studies; and royalties from Up To Date. AW reports grants from Agenus, Gilead, Genocea, Sanofi, and Vical to conduct clinical research studies. AW receives royalties from Up To Date. AW is an NIH grant recipient (NIH AI30731 and AI071113) and a consultant for Aicuris, Eisai, and Amgen.
Peer reviewers
Giuseppe Pizzo, DDS
Associate Professor
Department of Surgical, Oncological and Oral Sciences
School of Dentistry
University of Palermo
Palermo
Italy
Disclosures
GP declares that he has no competing interests.
Paul Adamson, MD, MPH
Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
PA declares that he has no competing interests.
Nicholas Van Wagoner, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Alabama
Birmingham
AL
Disclosures
NVW declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Morbidity and mortality weekly report: sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Jul 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Patel R, Kennedy OJ, Clarke E, et al. 2017 European guidelines for the management of genital herpes. Int J STD AIDS. 2017 Dec;28(14):1366-79.Full text Abstract
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 220: management of genital herpes in pregnancy. May 2020 [internet publication].Full text
British Association for Sexual Health & HIV; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of genital herpes in pregnancy. Oct 2014 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Syphilis
- Chancroid
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in adults and adolescents with HIV
- Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021
More GuidelinesPatient information
Cold sores
Genital herpes
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer