Resumo
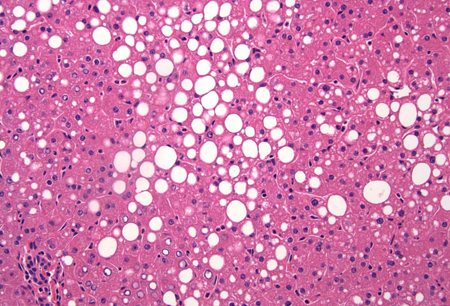
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- ausência de consumo significativo de bebidas alcoólicas
- anormalidade leve nos testes da função hepática
- obesidade troncular
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- fadiga e mal-estar
- desconforto abdominal no quadrante superior direito
- hepatoesplenomegalia
- sinais de doença hepática crônica
Fatores de risco
- obesidade
- resistência insulínica ou diabetes
- dislipidemia
- hipertensão
- síndrome metabólica
- perda de peso rápida
- uso de determinados medicamentos
- nutrição parenteral total (NPT)
- doenças associadas à DHG
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- aspartato aminotransferase (AST) e alanina aminotransferase (ALT) séricas
- bilirrubina total
- fosfatase alcalina
- gama-glutamiltransferase
- Hemograma completo
- perfil metabólico
- perfil lipídico
- tempo de protrombina (TP) e razão normalizada internacional (INR)
- albumina sérica
- perfil de doença hepática autoimune
- perfil de ferro
- antígeno de superfície da hepatite B, anticorpo anti-superfície e anticorpo anti-núcleo
- anticorpo do vírus da hepatite C
- nível de alfa 1-antitripsina e fenótipo
- ultrassonografia do fígado
Investigações a serem consideradas
- insulina em jejum
- cálculo do modelo de avaliação de homeostase (HOMA)
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) abdominal
- elastografia
- biópsia hepática
- ceruloplasmina
- Teste de mutação genética no gene HFE
- anticorpo anti-M2 mitocondrial
Novos exames
- fragmentos de citoqueratina-18
Algoritmo de tratamento
sem doença hepática em estágio terminal
doença hepática em estágio terminal
Colaboradores
Autores
Shahid M. Malik, MD

Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition
Department of Medicine
Program Director, Transplant Hepatology Fellowship Program
Starzl Transplantation Institute
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Declarações
SMM declares that he has no competing interests.
Kapil B. Chopra, MD, FACP, FAASLD, AGAF

Professor of Medicine
Medical Director of Comprehensive Liver Program and Liver Pancreas Institute
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Declarações
KBC declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Shahid M. Malik and Dr Kapil B. Chopra would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rachel Zhuang, a previous contribution to this topic.
Declarações
RZ declares no competing interests.
Revisores
Philip Newsome, PhD, FRCPE
Senior Lecturer in Hepatology & Honorary Consultant Physician
Liver Research Group
Institute of Biomedical Research
The Medical School
University of Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Declarações
PN declares that he has no competing interests.
Stephen A. Harrison, MD, LTC, MC
Chief of Hepatology
Department of Medicine
Gastroenterology & Hepatology Service
Brooke Army Medical Center
Fort Sam Houston
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
Houston
TX
Declarações
SAH is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Robert D. Goldin, MBCHB, MD, FRCPath
Reader in Liver and GI Pathology
Imperial College at St. Mary's
London
UK
Declarações
RDG declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, et al. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.Texto completo Resumo
Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, et al. NASPGHAN clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Feb;64(2):319-34.Texto completo Resumo
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016 Jun;64(6):1388-402.Texto completo Resumo
Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jan;112(1):18-35.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Doença hepática relacionada ao álcool
- Cirrose criptogênica
- Hepatite autoimune
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): assessment and management
- Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Mais DiretrizesCalculadoras
Escore MELDNa (para fins de listagem de transplantes de fígado, não é adequado para pacientes com menos de 12 anos de idade ) (unidades SI)
Mais CalculadorasConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal