Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- dispneia
- tosse produtiva
- febre
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- dor torácica
- expansão assimétrica do tórax
- frêmito reduzido
- egofonia
- pectorilóquia áfona
- estertores ou roncos
- taquicardia
- mal-estar/anorexia
Fatores de risco
- controle ineficiente da infecção/higiene das mãos
- intubação e ventilação mecânica; pressão do manguito endotraqueal <20 cm H₂O
- posição supina
- higiene bucal ineficiente
- sedação/ausência de interrupção da sedação
- intubação/reintubação
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
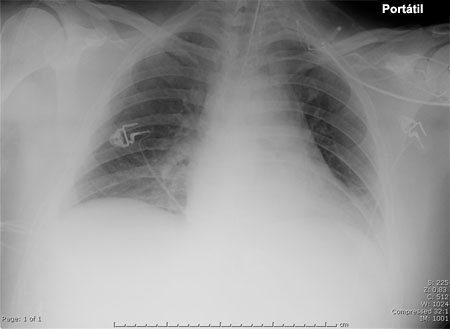
- radiografia torácica
- contagem diferencial de leucócitos
- oximetria de pulso
- cultura de amostra do trato respiratório inferior
Investigações a serem consideradas
- gasometria arterial
- toracocentese diagnóstica
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) do tórax
- proteína C-reativa
- ultrassonografia do pulmão
Novos exames
- Swab nasal para MRSA
Algoritmo de tratamento
antes dos resultados da cultura: sem fatores de risco para patógeno resistente a múltiplos medicamentos
antes dos resultados da cultura: com fatores de risco para patógeno resistente a múltiplos medicamentos, incluindo Pseudomonas e Staphylococcus aureus resistente à meticilina (MRSA)
após os resultados da cultura: devido a patógeno Gram-negativo
após os resultados da cultura: devido ao patógeno Gram-positivo
Colaboradores
Autores
Forest W. Arnold, DO, MSc, FIDSA

Professor of Medicine
Chief, Division of Infectious Diseases
Director Infectious Diseases Fellowship Training Program
Department of Medicine
School of Medicine
University of Louisville
Louisville
KY
Declarações
FWA declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Krishna Sundar, MD, FCCP
Associate Professor (Clinical)
Department of Medicine
University of Utah
Director
Pulmonary and Critical Care Research
IHC Urban South
Utah Valley Pulmonary Clinic
UT
Declarações
KS declares that he has no competing interests.
Ozan Akca, MD
Director of Research
Associate Professor
Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine
Neuroscience and Anesthesia Intensive Care Unit
University of Louisville
Louisville
KY
Declarações
OA declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 1;63(5):e61-111.Texto completo Resumo
Klompas M, Branson R, Cawcutt K, et al. Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-associated events, and nonventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2022 Jun;43(6):687-713.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Doença do coronavírus 2019 (COVID-19)
- Edema pulmonar cardiogênico
- Síndrome do desconforto respiratório agudo
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia, ventilator-associated events, and nonventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia in acute-care hospitals
- Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Pneumonia
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Dispositivos nas vias aéreas supraglóticas - Vídeo de demonstração
Via aérea nasofaríngea - Vídeo de demonstração
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal