Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- absence of significant alcohol use
- mild abnormality in liver function tests
- truncal obesity
Other diagnostic factors
- fatigue and malaise
- right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort
- hepatosplenomegaly
- signs of chronic liver disease
Risk factors
- obesity
- insulin resistance or diabetes
- dyslipidemia
- hypertension
- metabolic syndrome
- rapid weight loss
- use of certain drugs
- total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
- diseases associated with SLD
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- total bilirubin
- alkaline phosphatase
- gamma glutamyl transferase
- CBC
- metabolic panel
- lipid panel
- prothrombin time and INR
- serum albumin
- autoimmune liver disease screen
- iron studies
- hepatitis B surface antigen, surface antibody, and core antibody
- hepatitis C virus antibody
- alpha-1 antitrypsin level and phenotype
- liver ultrasound
Tests to consider
- fasting insulin
- homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) calculation
- abdominal MRI
- elastography
- liver biopsy
- ceruloplasmin
- HFE gene mutation testing
- anti-M2 mitochondrial antibody
Emerging tests
- cytokeratin-18 fragments
Treatment algorithm
without end-stage liver disease
end-stage liver disease
Contributors
Authors
Shahid M. Malik, MD

Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition
Department of Medicine
Program Director, Transplant Hepatology Fellowship Program
Starzl Transplantation Institute
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
SMM declares that he has no competing interests.
Kapil B. Chopra, MD, FACP, FAASLD, AGAF

Professor of Medicine
Medical Director of Comprehensive Liver Program and Liver Pancreas Institute
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
KBC declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Shahid M. Malik and Dr Kapil B. Chopra would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rachel Zhuang, a previous contribution to this topic.
Disclosures
RZ declares no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Philip Newsome, PhD, FRCPE
Senior Lecturer in Hepatology & Honorary Consultant Physician
Liver Research Group
Institute of Biomedical Research
The Medical School
University of Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
PN declares that he has no competing interests.
Stephen A. Harrison, MD, LTC, MC
Chief of Hepatology
Department of Medicine
Gastroenterology & Hepatology Service
Brooke Army Medical Center
Fort Sam Houston
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
SAH is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Robert D. Goldin, MBCHB, MD, FRCPath
Reader in Liver and GI Pathology
Imperial College at St. Mary's
London
UK
Disclosures
RDG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, et al. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.Full text Abstract
Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, et al. NASPGHAN clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Feb;64(2):319-34.Full text Abstract
European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Association for the Study of Diabetes; European Association for the Study of Obesity. EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016 Jun;64(6):1388-402.Full text Abstract
Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jan;112(1):18-35.Full text Abstract
LaBrecque DR, Abbas Z, Anania F, et al; World Gastroenterology Association. World Gastroenterology Organisation global guidelines: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul;48(6):467-73.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
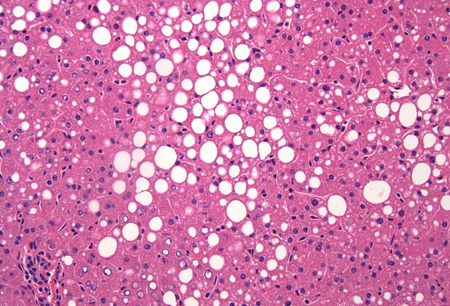
Differentials
- Alcohol-related liver disease
- Cryptogenic cirrhosis
- Autoimmune hepatitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- AASLD practice guideline on imaging-based non-invasive liver disease assessments of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis
- AASLD practice guideline on non-invasive liver disease assessments of portal hypertension
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer