Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- staring spells or inattention
- tonic-clonic seizures
- brief, arrhythmic muscular jerking movements
- eyes rolling back in head
- intercurrent illness
- unexplained falls
Other diagnostic factors
- incontinence
- tongue biting
- postictal phenomena
- seizure precipitated by fatigue or lack of sleep
- seizure precipitated by light or noise
- developmental delay
- neurocutaneous stigmata
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition or family history
- prenatal or perinatal insults
- metabolic/neurodegenerative disorders
- traumatic brain injury
- structural abnormalities of the central nervous system (CNS)
- neurocutaneous syndromes
- history of febrile seizures
- autistic spectrum disorder
- CNS infection
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- electroencephalogram (EEG)
- blood glucose level
- basic metabolic panel
- CBC
- ECG
Tests to consider
- MRI brain
- CT brain
- genetic testing
Treatment algorithm
acute repetitive seizures (children >1 month of age)
epilepsy syndromes with onset in infancy (1 month to 2 years)
epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood (2-12 years)
epilepsy syndromes with onset at a variable age
unidentified epilepsy syndrome
Contributors
Authors
Katherine C. Nickels, MD
Associate Professor, Neurology
EEG Lab Director
Child and Adolescent Neurology Residency Recruitment Chair
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
KCN has received travel compensation for attending advisory board meetings for Biocodex, Zogenix/UCB, and Takeda pharmaceuticals and will be receiving compensation for participating in advisory board meeting for Longboard. She receives compensation for participating in the J. Kiffin Penry Epilepsy Education Programs. She received hotel compensation for participating in CME education symposium through Miller Medical Communications, LLC, sponsored by UCB. She has received and will receive hotel compensation for participating in the Jack Pellock Resident on Pediatric Epilepsy Seminar through the Child Neurology Society. She is on the professional advisory board for the Epilepsy Foundation of Minnesota and receives no compensation. She serves as an assistant editor for Epilepsy Currents, for which she has not received compensation. She has participated in research and innovation for SEER medical and receives no compensation or royalties. She is an author of references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Katherine C. Nickels would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Leena Mewasingh, Dr Alla Nechay, and Dr Ewa Posner, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
LM attended educational events hosted by Eisai and Novartis. AN and EP declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Adam L. Hartman, MD
Assistant Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics
Johns Hopkins Hospital
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
AH has received research support from the National Institutes of Health that is greater than 6 figures. ALH's research is funded in part by the National Institutes of Health. He is the co-author of one review that is referenced in this topic.
Roger Weis, MD
Pediatric Neurologist
Kinderneurologisches Zentrum Mainz
Mainz
Germany
Disclosures
RW declares that he has no competing interests.
John Stephenson, MA, BM, DM, FRCP, HonFRCPCH
Consultant
Paediatric Neurology Emeritus
Fraser of Allander Neurosciences Unit
Royal Hospital for Sick Children
Honorary Professor in Paediatric Neurology and Senior Research Fellow
Department of Child Health
Division of Developmental Medicine
University of Glasgow
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
JS declares that he has no competing interests.
Anna Basu, BM, BCh, PhD, MA, MRCPCH
Honorary Clinical Lecturer
Paediatric Neurology
Newcastle General Hospital
Newcastle-upon-Tyne
UK
Disclosures
AB has previously worked as part of a clinical team with Dr Ewa Posner, a previous contributor to this topic. AB declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Scheffer IE, Berkovic S, Capovilla G, et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia. 2017 Apr;58(4):512-21.Full text Abstract
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA, et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia. 2017 Apr;58(4):522-30.Full text Abstract
Wirrell EC, Nabbout R, Scheffer IE, et al. Methodology for classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with list of syndromes: report of the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. 2022 Jun;63(6):1333-48.Full text Abstract
Hirsch E, French J, Scheffer IE, et al. ILAE definition of the idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes: position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. 2022 Jun;63(6):1475-99.Full text Abstract
Gaillard WD, Chiron C, Cross JH, et al; ILAE Committee for Neuroimaging, Subcommittee for Pediatric Neuroimaging. Guidelines for imaging infants and children with recent-onset epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2009 Sep;50(9):2147-53.Full text Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: seizures and epilepsy. 2019 [internet publication].Full text
Zuberi SM, Wirrell E, Yozawitz E, et al. ILAE classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in neonates and infants: position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. 2022 Jun;63(6):1349-97.Full text Abstract
Specchio N, Wirrell EC, Scheffer IE, et al. International League Against Epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood: position paper by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. 2022 Jun;63(6):1398-442.Full text Abstract
Kossoff EH, Zupec-Kania BA, Auvin S, et al; Charlie Foundation; Matthew's Friends; Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Optimal clinical management of children receiving dietary therapies for epilepsy: updated recommendations of the International Ketogenic Diet Study Group. Epilepsia Open. 2018 Jun;3(2):175-92.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
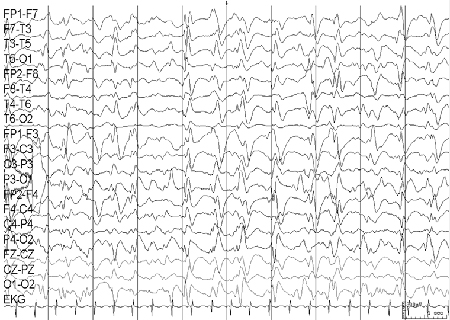
Differentials
- Functional seizures (nonepileptic seizures)
- Breath-holding spells (prolonged cyanotic expiratory apnea)
- Long QT syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Teratogenesis, perinatal, and neurodevelopmental outcomes after in utero exposure to antiseizure medication
- Epilepsies in children, young people and adults
More GuidelinesPatient information
Epilepsy: what is it?
Febrile seizures
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer