Resumo
Definição
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- fevers and night sweats
- weight loss
- skin rashes and post-inflammatory scars
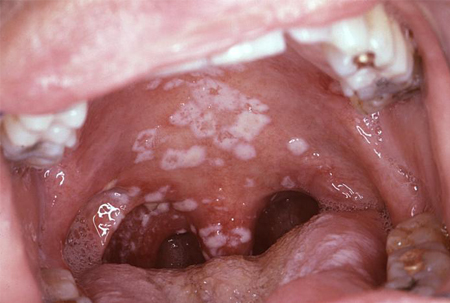
- oral ulcers, angular cheilitis, oral thrush, or oral hairy leukoplakia
- diarrhea
- changes in mental status or neuropsychiatric function
- recent hospital admissions
- tuberculosis (TB)
- medical comorbidities
- generalized lymphadenopathy
- genital sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- chronic vaginal candidiasis
- shingles
- wasting syndrome
- headaches
- Kaposi sarcoma
- periodontal disease
- retinal lesions on fundoscopy
- shortness of breath on exertion, cyanosis on exertion, dry cough, silent chest on auscultation
Other diagnostic factors
- peripheral neuropathy
- recurrent herpes simplex
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
- meningeal signs (bacterial or viral meningitis)
Risk factors
- unprotected anal intercourse
- unprotected penile-vaginal sexual intercourse
- gay men and other men who have sex with men (MSM)
- transgender people
- commercial sex worker
- people who inject drugs
- coinfection with other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- people living in prisons
- percutaneous needle stick injury
- racial and ethnic minorities
- use of progestin-only injectable contraceptives
- cosmetic injection procedures
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- fourth-generation HIV antigen/antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- HIV-1/HIV-2 antibody differentiation immunoassay
- HIV nucleic acid test
- CD4 count
- serum viral load (HIV RNA)
- drug resistance testing
- pregnancy test
- serum hepatitis B serology
- serum hepatitis C serology
- hepatitis A serology (IgG)
- toxoplasma serology (IgG)
- CBC with differential
- basic metabolic panel
- urinalysis
- liver function tests (LFTs)
- random or fasting plasma glucose
- lipid profile
- human leukocyte antigen-B*5701 testing
- testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) including mpox
Tests to consider
- chest x-ray
- testing for tuberculosis
- testing for cryptococcosis
Treatment algorithm
newly confirmed diagnosis
virologic suppression achieved
virologic or immunologic treatment failure
Contributors
Authors
Chad J. Achenbach, MD, MPH
Professor of Medicine, Preventive Medicine, and Biomedical Engineering
Infectious Diseases
Northwestern Medicine
Feinberg School of Medicine
McCormick School of Engineering
Northwestern University
Evanston and Chicago
IL
Disclosures
CJA declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Chad J. Achenbach would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard Rothman, Dr Michael Ehmann, Dr Linda-Gail Bekker, Dr Catherine Orrell, and Dr Lisa Capaldini, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
ME, LGB, and CO declare that they have no competing interests. RR attended a symposium/conference hosted by a funding agency, Gilead HIV FOCUS program, from which he receives research funds. RR pays staff for an implementation/research program grant from Gilead HIV FOCUS for development of HIV testing programs in Emergency Departments. LC is on the speakers' bureau for the following pharmaceutical companies: GlaxoSmithKline, BMS, Merck, Gilead, Roche, Pfizer, Solvay, Lilly, Serrano, and Tibotec.
Peer reviewers
Michael Horberg, MD, MAS, FACP, FIDSA
Associate Medical Director
Kaiser Permanente Mid-Atlantic Permanente Medical Group
Oakland
CA
Disclosures
MH declares that he has no competing interests
Roy Gulick, MD
Professor of Medicine
Chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases
Weill Cornell Medicine
New York
NY
Disclosures
RG declares that he has no competing interests
Marianne Harris, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of British Columbia
Vancouver
Canada
გაფრთხილება:
MH is a member of an advisory board and/or speakers' bureau for Gilead Sciences Canada Inc, Merck Canada Inc, and ViiV Healthcare.
Jeremy Day, BChir, MB
Infectious Disease Physician
Oxford University Clinical Research Unit
Hospital for Tropical Diseases
Ho Chi Minh City
Vietnam
Disclosures
JD declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
World Health Organization. Guideline on when to start antiretroviral therapy and on pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV. Sep 2015 [internet publication].Full text
US Department of Health and Human Services Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents with HIV. Sep 2025 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Cytomegalovirus infection (CMV)
- Influenza infection
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents with HIV
- CDC Yellow Book: health information for international travel - travelers with HIV
More GuidelinesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
HIV: what is it?
HIV: testing
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal