შეჯამება
განსაზღვრება
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- asymptomatic
- polydipsia
- polyuria
- unintentional weight loss
- polyphagia
- hyperglycemic crisis
Other diagnostic factors
- fatigue
- blurred vision
- nocturia
- candidal infections
- skin infections
- urinary tract infections
- paresthesias
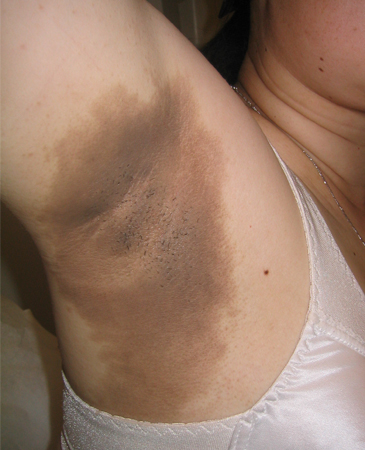
- acanthosis nigricans
Risk factors
- older age
- overweight/obesity
- gestational diabetes
- prediabetes
- first-degree relative with type 2 diabetes
- African, Latino, Asian or American-Indian ancestry
- physical inactivity
- polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- hypertension
- dyslipidemia
- cardiovascular disease
- stress
- smoking
- suboptimal sleep
- low levels of testosterone/hypogonadism in men
- mental illness
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- HbA1c
- fasting plasma glucose
- 2-hour plasma glucose
- random plasma glucose
Tests to consider
- urine ketones
- random C-peptide
- autoantibodies
- urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR)
- serum creatinine and estimated GFR (eGFR)
- fasting lipid profile
- ECG
- B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)/N-terminal prohormone B-natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP)
- ankle-brachial index (ABI)
- toe-brachial index (TBI)
- dilated retinal examination
- liver function test (LFT)
- platelet count
- noninvasive tests of liver elasticity
Treatment algorithm
at initial diagnosis
marked hyperglycemia nonpregnant: serum glucose ≥300 mg/dL (≥16.7 mmol/L) or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) >10% (>86 mmol/mol) or symptomatic
without marked hyperglycemia nonpregnant asymptomatic: serum glucose <300 mg/dL (<16.7 mmol/L) or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) <10% (<86 mmol/mol)
pregnant
Contributors
Authors
Klara R. Klein, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor
Director
Endocrine Diabetes and Obesity Clinical Research Unit (EnDO CRU)
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine
University of North Carolina
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
KRK is supported by the University of North Carolina Department of Medicine and School of Medicine Physician Scientist Training Program and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health, through grant K12TR004416. KRK has received personal compensation for consultation from Novo Nordisk and Roche Pharmaceuticals. Additionally, KRK has received research related contracts (paid to the institution) from NCATS, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Carmot, Diasome, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and vTv Therapeutics.
Brooke C. Matson, MD, PhD
Fellow
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine
University of North Carolina
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
BCM has received research grant funding from the Endocrine Fellows Foundation. BCM has received travel support from the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society to attend their annual meetings (2023 and 2024, respectively) and from Diabetes Dialog, hosted by the Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes at the University of Colorado, to attend their fellow curriculum (2023).
Acknowledgements
Dr Klara R. Klein and Dr Brooke C. Matson would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Gregg Simonson, Dr Anders Carlson, Dr Thomas Martens, Dr Richard Bergenstal, Dr Patrick J. O'Connor, and Dr JoAnn M. Sperl-Hillen, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
GS declares that his employer, HealthPartners Institute dba International Diabetes Center, has organizational interests that include receiving unrestricted educational grants from Abbott Diabetes Care and Sanofi. GS receives no personal income from any of these activities. AC is employed by HealthPartners Institute and Fabric. HealthPartners Institute has received payments on AC's behalf for research and/or consulting services from Abbott Diabetes, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Medtronic, Insulet, Tandem Diabetes, Mannkind, and United Health Group. All research or consulting fees are paid directly to HealthPartners Institute. AC receives no personal income from any of these services. AC is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. HealthPartners Institute employs TM and has contracts with Abbott Diabetes Care, Dexcom, Insulet, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi US Services, Inc., and Tandem for his services as a research investigator, speaker, and/or consultant. No personal income from any of these services goes to TM. TM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. RB has received research support, has acted as a consultant, or has been on the scientific advisory board for Abbott Diabetes Care, Ascensia, Bigfoot Biomedical, Inc., CeQur, DexCom, Eli Lilly, Hygieia, Insulet, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Onduo, Roche Diabetes Care, Tandem Diabetes Care, Sanofi, United Healthcare, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, and Zealand Pharma. RB's employer, nonprofit HealthPartners Institute, contracts for his services and he receives no personal income. RB is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. PJO receives research funding from the National Institutes of Health on multiple projects. JMS-H is an inventor on a US patent for Disease Treatment Simulation, a simulation-based technology developed without commercial support to educate health providers on chronic disease management in a virtual environment. PJO and JMS-H are authors of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
David K. McCulloch, MD
Medical Director
Clinical Improvement Group Health Cooperative
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
DKM declares that he has no competing interests.
Ashim K. Sinha, MBBS, MD, FRACP, FACE
Associate Professor
Director of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Cairns Base Hospital and Diabetes Centre
Queensland
Australia
Disclosures
AKS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes Care. 2025 Jan 1;48(suppl 1):S1-336.Full text
Cappola AR, Auchus RJ, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, et al. Hormones and aging: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jul 14;108(8):1835-74.Full text Abstract
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2022 Nov 1;45(11):2753-86.Full text Abstract
US Preventive Services Task Force. Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: screening. Aug 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Qaseem A, Obley AJ, Shamliyan T, et al. Newer pharmacologic treatments in adults with type 2 diabetes: a clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2024 May;177(5):658-66.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Prediabetes
- Diabetes mellitus, type 1
- Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- IDF global clinical practice recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes - 2025
- IDF global clinical practice recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes - 2025
More GuidelinesPatient information
Prediabetes
Diabetes: what is it?
More Patient informationCalculators
Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimation (eGFR) by Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Equation with Creatinine, without Race (2021)
Cirrhosis probability in hepatitis C (FIB-4)
More CalculatorsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer