小结
定义
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- 存在的危险因素
- 40 岁以上男性
- 人工作业困难
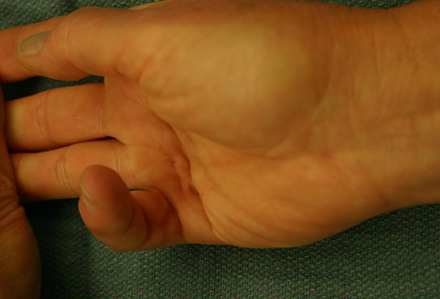
- 手掌结节
- 手掌皮肤病变
- 键周索
- MCP 关节挛缩
- 近端指间 (PIP) 关节挛缩
- Hueston 桌面试验阳性
其他诊断因素
- 双侧受累
- Garrod 结
- 足部趾面受累
- 阴茎受累
危险因素
- 男性
- 年龄>40 岁
- 家族史
- 糖尿病
- 高酒精摄入量
- 吸烟
- 创伤
- 抗惊厥药
诊断性检查
需考虑的检查
- 手部超声
治疗流程
无 MCP 关节或 PIP 关节挛缩
30°及以下的 MCP 关节挛缩且无 PIP 关节挛缩
30°以上的 MCP 关节挛缩和/或 PIP 关节挛缩
撰稿人
作者
Craig M. Rodner, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
University of Connecticut Health Center/New England Musculoskeletal Institute
Farmington
CT
利益声明
CMR declares that he has no competing interests.
鸣谢
Dr Craig M. Rodner would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Thomas H. Trojian and Dr Daniel M. Avery, both previous contributors to this topic. THT and DMA declare that they have no competing interests.
同行评议者
Carlos Wigderowitz, MD, PhD, FRCSEd
Senior Clinical Lecturer in Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery
Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery
TORT Centre
Ninewells Hospital
Dundee
UK
利益声明
CW declares that he has no competing interests.
Bill Townley, MD
Specialist Registrar
Plastic Surgery
Salisbury District Hospital
Salisbury
UK
利益声明
BT is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Zhongyu Li, MD
Assistant Professor
Orthopaedics
Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center
Winston-Salem
NC
利益声明
ZL declares that he has no competing interests.
鉴别诊断
- 扳机指
- 上皮样肉瘤
- 屈曲指
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- 荷兰掌腱膜挛缩症多学科指南
- 早期掌腱膜挛缩症的放射疗法
更多 指南登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明