Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- polyuria
- polydipsia
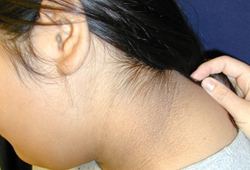
- acanthosis nigricans
- nocturia
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- hypertension
- yeast infections
- skin infections
- urinary tract infections
- fatigue
- blurred vision
- weight loss
Factores de riesgo
- obesity
- genetic predisposition/family history
- African-American, Hispanic, American-Indian, and Asian or Pacific Islander
- puberty
- female sex
- diabetic in-utero environment
- small for gestational age
- rapid growth in infancy
- bottle feeding
- high protein intake in infancy
- polycystic ovaries
- intramyocellular lipid content
- fat deposition in the liver
- learning disability
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- urine dipstick
- random plasma glucose
- fasting plasma glucose
- HbA1c
- autoantibodies to insulin, islet antigen (IA-2), glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), and zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8)
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- 2-hour plasma glucose
- random C-peptide
Algoritmo de tratamiento
ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS)
HbA1c <8.5%: no acidosis or ketosis
HbA1c ≥8.5%: no acidosis with or without ketosis
Colaboradores
Autores
Jennifer Miller, MD

Professor
Department of Pediatrics
University of Florida
Gainesville
FL
Divulgaciones
JM declares that she has received research funding from Soleno Therapeutics, Harmony Biosciences, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. JM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Chelsea Zimmerman, MD
Clinical Physician
Pediatric Endocrinology
Endocrinology and Metabolism of East Alabama
Opelika
AL
Divulgaciones
CZ declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimientos
Dr Jennifer Miller and Dr Chelsea Zimmerman would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Arlan Rosenbloom and Dr Paul Hiers, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
AR is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. Unfortunately, we have since been made aware that AR is deceased. PH declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Philip Zeitler, MD, PhD
Professor of Pediatrics and Clinical Science
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Divulgaciones
PZ declares that he has no competing interests.
Julian P. Hamilton-Shield, MB, ChB, MD(Bristol), MRCP, FRCPCH, FRCPCH
Professor
Diabetes and Metabolic Endocrinology
School of Clinical Sciences
University of Bristol
UK
Divulgaciones
In the past, JPHS received speaking honoraria from Sanofi-Aventis, Roche, Abbott, Novo Nordisk, and Nutricia. None of these talks were directly pertinent to the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Kristen Nadeau, MD
Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Divulgaciones
KN declares that she has no competing interests.
Dennis Styne, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Rumsey Chair of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of California
Sacramento
CA
Divulgaciones
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes care. 2025 Jan;48(suppl 1):S1-352.Texto completo
Shah AS, Barrientos-Pérez M, Chang N, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2024: type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Horm Res Paediatr. 2024;97(6):555-83.Texto completo Resumen
Glaser N, Fritsch M, Priyambada L, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2022: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022 Nov;23(7):835-56. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM)
- Monogenic diabetes: maturity-onset diabetes of the young
Más DiferencialesDiretrizes
- Standards of care in diabetes - 2025
- Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents
Más DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Diabetes type 2: should I take insulin?
Diabetes type 2: what are the treatment options?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal