最后审阅: 10 Feb 2025
最后更新: 15 Dec 2023
小结
定义
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- 童年与青春期
- 疼痛在几周至几个月内加重
- 肿块/肿胀
完整详情
其他诊断因素
- 男性
- 跛行
- 外伤史
- 关节活动度受限
- 皮肤表面溃疡
完整详情
危险因素
- 童年与青春期
- 佩吉特病
- 放射治疗
- Rothmund-Thomson 综合征
- 家族性视网膜母细胞瘤综合征
- Li-Fraumeni 综合征
- 纤维组织发育异常
- 化疗
- 男性
完整详情
诊断性检查
首要检查
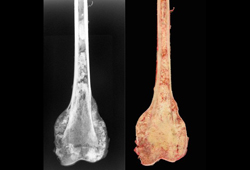
- 常规 X 光平片
- 骨活检
- 磁共振成像 (MRI)
- 计算机体层成像 (CT)
- 胸部 CT
- 骨扫描
- 全身 18F-脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)-PET/CT
- 全血细胞计数
- 血清碱性磷酸酶
- 血清乳酸脱氢酶
完整详情
治疗流程
急症处理
就诊时为低级别肿瘤
就诊时为高级别非转移性肿瘤
就诊时即为转移性肿瘤
持续性治疗
复发性疾病
撰稿人
作者
David Loeb, MD, PhD
Chief
Division of Pediatric Hematology, Oncology, and Marrow & Blood Cell Transplantation
Children's Hospital at Montefiore
Associate Professor, Pediatrics
Associate Professor, Developmental and Molecular Biology
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Bronx
NY
利益声明
DL declares that he has no competing interests.
鸣谢
Dr David Loeb would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Luminita Rezeanu and Dr Michael J. Klein, the previous contributors to this topic.
利益声明
LR and MJK declare that they have no competing interests.
同行评议者
Edward Sauter, MD, PhD
Professor of Surgery
Ellis Fischel Cancer Center
University of Missouri
Columbia
MO
利益声明
ES declares that he has no competing interests.
Rachael Windsor, BSc, MBBS, MSc, MRCPCH
Locum Consultant Paediatric Oncologist
University College Hospital
London
UK
利益声明
RW declares that she has no competing interests.
鉴别诊断
- 尤因氏肉瘤
- 软骨肉瘤
- 恶性纤维组织细胞瘤
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- NCCN 肿瘤学临床实践指南:骨癌
- 风湿病和肌肉骨骼疾病患者的疫苗接种指南
更多 指南登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明