最后审阅: 22 Dec 2024
最后更新: 22 Sep 2023
小结
定义
病史和体格检查
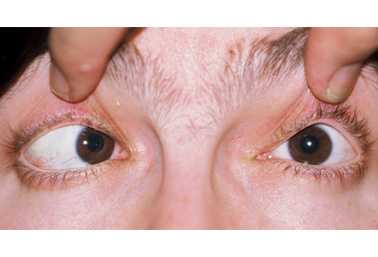
关键诊断因素
- 复视
- 眼偏视
- 弱视
完整详情
其他诊断因素
- 异常眼球运动
- 视觉模糊
- 视疲劳
- 一只眼的间歇性闭合
- 颅神经麻痹
完整详情
危险因素
- 斜视家族史
- 早产
- 低出生体重
- 母孕期吸烟
- 屈光不正
完整详情
诊断性检查
首要检查
- 遮盖试验
- 同时进行棱镜和遮盖试验 (SPCT)
- 去遮盖试验 (UCT)
- 交替棱镜遮盖试验 (APCT)
- 希尔施贝格试验
- 科日姆斯基试验
完整详情
需考虑的检查
- 双眼运动检查
- 转向试验
- 被动牵拉试验
- 眼眶 CT 或 MRI
- 头颅核磁共振成像
- 胸部 CT
完整详情
治疗流程
急症处理
原发性斜视
继发性斜视
撰稿人
作者
Daniel J. Salchow, MD

Director
Pediatric Ophthalmology; Strabismus; Neuro-ophthalmology
Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Berlin
Germany
利益声明
DJS declares that he has no competing interests.
同行评议者
Robert B. Avery, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology
Department of Surgery
University of New Mexico School of Medicine
Albuquerque
NM
利益声明
RBA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Tiffin, BMedSci(Hons), MBBS, FRCOphth
Ophthalmology Consultant
City Hospitals Sunderland
Sunderland
UK
利益声明
PT declares that he has no competing interests.
Jonathan Smith, MBBS, MRCP, MRCOphth
Specialist Registrar in Ophthalmology
Ophthalmics
Royal Victoria Infirmary
Newcastle
UK
利益声明
JS declares that he has no competing interests.
鉴别诊断
- 假性斜视
- 视力模糊
- 单眼复视
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- 小儿眼科/斜视的摘要基准 - 2022 年
- 弱视的首选实践方式
更多 指南登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明