Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
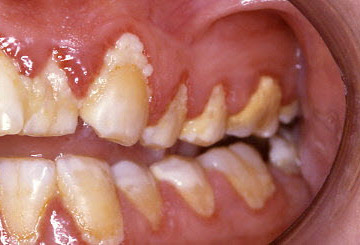
- bleeding on tooth brushing
- dental plaque
- necrosis and ulcers in free gingiva
Other diagnostic factors
- halitosis
- redness, swelling, and puffy gingiva
- pseudomembrane formation
- cervical lymphadenopathy
- fever
- malaise
- pain
Risk factors
- poor oral hygiene
- tobacco
- diabetes mellitus
- pregnancy
- severe malnutrition or marginal nutritional deficiencies
- HIV/AIDS (in necrotizing gingivitis [NG])
- stress (in necrotizing gingivitis [NG])
- severe (viral) infections (in necrotizing gingivitis [NG])
- previous history of necrotizing gingivitis (NG)
- stress (in plaque-induced gingivitis)
- xerostomic medications
- male sex
- extreme living conditions (necrotizing gingivitis [NG])
- high alcohol intake
- substance use
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- clinical diagnosis
Treatment algorithm
necrotizing gingivitis (NG)
non-necrotizing gingivitis
Contributors
Authors
Giuseppina Campisi, DDS, MS
Professor of Oral Diseases
Department of Surgical, Oncological and Oral Sciences
School of Dentistry
University of Palermo
Palermo
Italy
Disclosures
GC declares that she has no competing interests.
Giuseppe Pizzo, DDS
Associate Professor of Periodontology and Dental Public Health
Department of Surgical, Oncological and Oral Sciences
School of Dentistry
University of Palermo
Palermo
Italy
Disclosures
GP declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Giuseppina Campisi and Dr Giuseppe Pizzo would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Bruce L. Pihlstrom and Dr Alice E. Curran, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
BLP and AEC declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Gary Armitage, MD
Professor
Division of Periodontology
University of California
San Francisco
CA
Disclosures
GA declares that he has no competing interests.
Lynn Solomon, MD
Assistant Professor
Tufts University
Boston
MA
Disclosures
LS declares that she has no competing interests.
Donald J. DeNucci, DDS, MS
Program Director
Practice Based Research Networks
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
NIH
Bethesda
MD
Disclosures
DJD declares that he has no competing interests.
Stephen Porter, BSc, PhD, MD, FDSRCS, FDSRCSEd, FHEA
Institute Director
Professor of Oral Medicine
Academic Head, Oral Medicine and Special Needs Dentistry Unit
Honorary Consultant in Oral Medicine, UCLH NHS Foundation Trust
UCL Eastman Dental Institute
London
UK
Disclosures
SP declares that he has no competing interests.
Marco Carrozzo, MD, DSM
Professor of Oral Medicine
School of Dental Sciences
University of Newcastle Upon Tyne
UK
Disclosures
None declared
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Chapple ILC, Mealey BL, Van Dyke TE, et al. Periodontal health and gingival diseases and conditions on an intact and a reduced periodontium: Consensus report of workgroup 1 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Periodontol. 2018 Jun;89 Suppl 1:S74-84. Abstract
Farah CS, Balasumbramaniam R, McCullough MJ. Contemporary Oral Medicine. A Comprehensive Approach to Clinical Practice. 1st ed. New York, NY: Springer International Publishing; 2019.
Public Health England (PHE). Delivering better oral health: an evidence-based toolkit for prevention. 3rd ed. London: Department of Health; 2021.Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Oral lichen planus
- Pemphigoid
- Pemphigus
More DifferentialsPatient information
Bad breath
Quitting smoking
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer