Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- acute or chronic cough
- fever
- dyspnea
- wheezing
- crackles
Other diagnostic factors
- laryngospasm
Risk factors
- decreased level of consciousness (Glasgow coma scale score <9)
- increased severity of illness
- general anesthesia
- age >70 years
- male sex
- head trauma
- cerebrovascular disease
- endotracheal or tracheostomy tube
- dysphagia
- airway difficulties
- barium meal
- gastroesophageal reflux disease
- feeding tubes
- supine position
- delayed gastric emptying
- obesity
- drugs that reduce esophageal sphincter tone
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- chest x-ray
Tests to consider
- chest CT
- bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage
- CBC
- arterial blood gases
- blood culture
- thoracentesis
Treatment algorithm
pneumonitis due to aspiration of gastric contents
pneumonitis due to aspiration of barium
Contributors
Expert advisers
Augustine Lee, MD
Professor of Medicine
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
AL declares that he has no competing interests.
Spencer Deleveaux, MBBS
Fellow
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
SD declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Augustine Lee and Dr Spencer Deleveaux would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Madison Macht, Dr Kamran Mahmood, Dr Scott Shofer, Dr Septimiu Murgu, and Dr Henri Colt, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
MM, KM, SS, SM, and HC declare they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Andrew Parfitt, MBBS, FFAEM
Clinical Director
Acute Medicine
Associate Medical Director
Consultant Emergency Medicine
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
Clinical Lead and Consultant
Accident and Emergency Medicine
St Thomas' Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
AP declares that he has no competing interests.
Momen M. Wahidi, MD, MBA
Professor of Medicine
Pulmonary and Critical Care
Feinberg School of Medicine
Northwestern University
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
MMW declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 1;344(9):665-71. Abstract
Smith Hammond CA, Goldstein LB. Cough and aspiration of food and liquids due to oral-pharyngeal dysphagia: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2006 Jan;129(1 suppl):154S-68S. Abstract
American Society of Anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration: application to healthy patients undergoing elective procedures - an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists task force on preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration. Anesthesiology. 2017 Mar;126(3):376-93.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
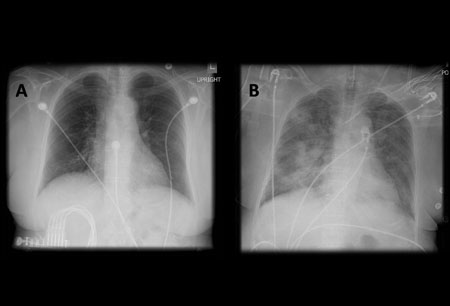
Differentials
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Asthma exacerbation
- Cystic fibrosis with exacerbation
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: dysphagia
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer