Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- headache
Other diagnostic factors
- seizures
- nuchal rigidity
- decreased level of consciousness
- focal neurologic deficit
Risk factors
- smoking
- moderate- to high-level alcohol consumption
- family history of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- previous subarachnoid hemorrhage
- heritable connective tissue disease
- hypertension
- head trauma
- intracranial infection
- tumor
- arteriovenous malformations or fistulas
- drug abuse
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CT head scan
- conventional catheter-based angiogram
- CT angiography
- magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Tests to consider
- lumbar puncture
Treatment algorithm
unruptured aneurysm
ruptured aneurysm
Contributors
Authors
Brendan Eby, MD
Assistant Professor
Departments of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Disclosures
BE has been a paid speaker at a national neurointervention fellows course sponsored by Penumbra Inc; the talk was unrelated to the sponsor's products or services.
Acknowledgements
Dr Eby would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Grasso and Dr Michael Chen, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
MC is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
David Altschul, MD
Chief of Neurovascular Surgery
Montefiore Medical Center
New York
NY
Disclosures
DA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Martin, MA, BM BCh, MD, FRCP
Consultant Neurologist
Addenbrookes Hospital
Cambridge
UK
Disclosures
PM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015 Aug;46(8):2368-400.Full text Abstract
Hoh BL, Ko NU, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. 2023 Guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023 Jul;54(7):e314-70.Full text Abstract
Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging., Ledbetter LN, Burns J, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Cerebrovascular diseases - aneurysm, vascular malformation, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 Nov;18(11s):S283-S304.Full text Abstract
Etminan N, de Sousa DA, Tiseo C, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines on management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Eur Stroke J. 2022 Sep;7(3):V.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
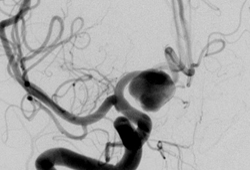
Differentials
- Arteriovenous malformation
- Hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Guidelines on management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms
More GuidelinesPatient information
Emergency treatment for a stroke
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer