小结
定义
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- 存在的危险因素
- 苍白
- 黄疸
- 脾肿大
其他诊断因素
- 疲劳
- 胎儿水肿或死胎
危险因素
- 脾切除术、贫血、黄疸或 HS 家族史
- 风险人群
诊断性检查
首要检查
- 全血细胞计数 (FBC)
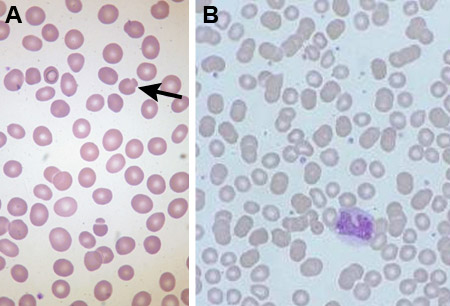
- 网织红细胞计数
- 血涂片
- 血清胆红素
- 血清转氨酶
- 直接抗人球蛋白试验 (DAT)
需考虑的检查
- 伊红-5-马来酰亚胺结合试验
- 酸化甘油溶解试验
- 十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳
新兴检查
- 遗传学分析
治疗流程
新生儿(<28 日龄)
婴儿(>28 日龄)、儿童和成人:重度 HS
婴儿(>28 日龄)、儿童和成人:轻度至中度 HS
撰稿人
作者
Shelley Crary, MD, MSCS
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock
AR
利益声明
SC is reimbursed for membership on a drug and safety monitoring board (Novartis) for a non-related drug.
鸣谢
Dr Shelley Crary would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Paula Bolton-Maggs, a previous contributor to this topic.
利益声明
PB-M has received travel and accommodation payments to give a series of lectures on paediatric haematology, one of which was on HS. She also was an expert witness in a legal case concerning a child with HS. PB-M is an author of some references cited in this topic.
同行评议者
Robert Schilling, MD
Professor of Medicine Emeritus
School of Medicine and Public Health
University of Wisconsin-Madison
Madison
WI
利益声明
RS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
鉴别诊断
- 非溶血性贫血
- 溶血性贫血的其他原因
- 球形细胞增多症的其他原因
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- 关于遗传性溶血性贫血中进行脾切除术的建议
- 关于实验室诊断非免疫遗传性红细胞膜疾病的 ICSH 指南
更多 指南患者教育信息
何为新生儿黄疸?
新生儿黄疸:如何有效治疗?
更多 患者教育信息登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明
