Резюме
Определение
Анамнез и осмотр
Ключевые диагностические факторы
- наличие факторов риска
- олигурия или анурия
- гипотензия
- тахикардия
Другие диагностические факторы
- плохое пероральное возмещение и анорексия
- недомогание
- жажда
- головокружение
- ортопноэ/диспноэ
- отек
Факторы риска
- хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП)
- хроническая гипертония
- сахарный диабет
- пожилой возраст
- состояния с низкой перфузией
- сепсис
- обширное оперативное вмешательство
- воздействие нефротоксических веществ
- воздействие рентгенконтрастных препаратов
- воздействие эндогенных токсинов
Диагностические исследования
Исследования, которые показаны в первую очередь
- основной метаболический профиль (включая мочевину и креатинин)
- отношение мочевина/креатинин
- концентрация натрия в моче
- осмоляльность мочи
- фракционная экскреция натрия
- фракционная экскреция мочевины
- анализ осадка мочи
- развернутый анализ крови
- коагулограмма
- миоглобин в моче
Исследования, проведение которых нужно рассмотреть
- газы артериальной крови (ГАК)
- исследования агрегации тромбоцитов
- УЗИ
- ЭКГ
- диаметр нижней полой вены (НПВ), измеренный с помощью УЗИ
- биопсия почки
- биомаркеры сыворотки крови и мочи
Алгоритм лечения
острый тубулярний некроз (ОТН)
Составители
Авторы
Maria Jesus Lloret Cora, MD, MSc
Consulting Staff
Nephrology Department
Fundació Puigvert
Barcelona
Spain
Раскрытие информации
MJLC declares that she has no competing interests.
Leonor Fayos de Arizon, MD
Resident
Nephrology Department
Fundació Puigvert
Barcelona
Spain
Раскрытие информации
LFA declares that she has no competing interests.
Выражение благодарностей
Dr Maria Jesus Lloret Cora would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Roser Torra, the previous contributor to this topic.
Раскрытие информации
RT declares that she has no competing interests.
Рецензенты
Ajay Kumar, MD, FACP
Medical Director
Blood Management
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland
OH
Раскрытие информации
AK has received a fee for speaking about perioperative blood management from Ortho-Biotech and has also received reimbursement from medscape.com for the education webcast of the same presentation.
Irfan Moinuddin, MD
Assistant Professor
Chicago Medical School
Rosalind Franklin University
Lombard
IL
Раскрытие информации
IM declares that he has no competing interests.
Robert Tompkins, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Family Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
Tyler
TX
Раскрытие информации
RT declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
Список литературы
Основные статьи
Gill N, Nally JV Jr, Fatica RA. Renal failure secondary to acute tubular necrosis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Chest. 2005 Oct;128(4):2847-63. Аннотация
Статьи, указанные как источники
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
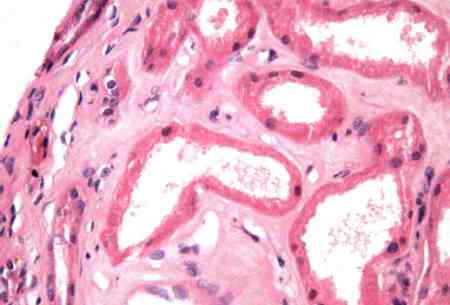
Отличия
- Преренальная азотемия
- Истинная почечная азотемия
Больше ОтличияРекомендации
- KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury
Больше РекомендацииВойдите в учетную запись или оформите подписку, чтобы получить полноценный доступ к BMJ Best Practice
Использование этого контента попадает под действие нашего заявления об отказе от ответственности