Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of exposure
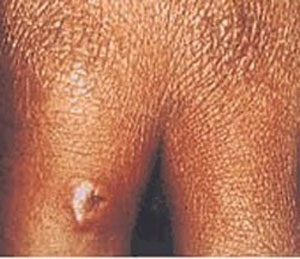
- necrotic skin lesions (cutaneous)
- painless lesions (cutaneous)
- edema (cutaneous)
- influenza-like illness (inhalation)
- respiratory symptoms (inhalation)
- oropharyngeal ulceration (ingestion)
Other diagnostic factors
- lymphadenopathy
- signs of meningitis
- hypotension
- gastrointestinal symptoms (ingestion)
Risk factors
- environmental exposure
- occupational exposure
- biologic terrorism
- undercooked meat ingestion
- heroin use
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- culture and Gram stain
- real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
- serology
- anthrax lethal factor (LF) toxin mass spectrometry
- biopsy
- CBC
- chest x-ray
Tests to consider
- CT chest
Treatment algorithm
cutaneous anthrax without signs/symptoms of meningitis
systemic anthrax with or without meningitis
Contributors
Authors
Kari Simonsen, MD, MBA
Professor of Pediatric Infectious Diseases
University of Nebraska Medical Center
Omaha
NE
Disclosures
KS declares that she has organizational financial interests for sponsored clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccines (Pfizer/BioNTech), investigational antibiotics (Melinta Therapeutics), and RSV vaccine (Sanofi/AstraZeneca), none of which are related to anthrax.
Clayton Mowrer, DO, MBA
Fellow
Division of Internal Medicine/Pediatric Infectious Diseases
University of Nebraska Medical Center
Omaha
NE
Disclosures
CM declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Kari Simonsen and Dr Clayton Mowrer would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Daniel Boyle, Dr Brian Wolf, Dr Teresa Zembower, and Dr Pavani Reddy, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
DB, BW, TZ, and PR declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Timothy Benton, MD
Regional Chairman
Residency Program Director
Associate Professor
Family and Community Medicine
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at the Permian Basin
Odessa
TX
Disclosures
TB declares that he has no competing interests.
Raffaele D’Amelio, MD
Professor of Internal Medicine
Director: Unit Clinical Immunology and Allergy
Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine
Sapienza University of Rome, S. Andrea University Hospital
Rome
Italy
Disclosures
RD declares that he has no competing interests.
Ali Hassoun, MD, FACP, FIDSA, AAHIVS
Infectious Disease Specialist
Alabama Infectious Diseases Center
Huntsville
AL
Declarações
AH declares that he has no competing interests.
Tim Brooks, MA, LMSSA, MB BChir, MSc, FRCPath, FRSPH
Head of Novel & Dangerous Pathogens
Novel and Dangerous Pathogens
HPA Centre for Emergency Preparedness and Response
Salisbury
UK
Declarações
TB declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Bower WA, Yu Y, Person MK, et al. CDC guidelines for the prevention and treatment of anthrax, 2023. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2023 Nov 17;72(6):1-47.Texto completo Resumo
Bower WA, Schiffer J, Atmar RL, et al; ACIP Anthrax Vaccine Work Group. Use of anthrax vaccine in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2019. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2019 Dec 13;68(4):1-14.Texto completo Resumo
World Health Organization. Anthrax in humans and animals. 4th ed. 2008 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Bacterial furunculosis
- Ecthyma gangrenosum
- Orf (ecthyma contagiosum)
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- CDC Yellow Book: health information for international travel - anthrax
- CDC guidelines for the prevention and treatment of anthrax
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal