Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- sexo masculino
- história de doença inflamatória intestinal
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- idade 25-45 anos
- dor abdominal
- prurido
- fadiga
- perda de peso
- febre
- icterícia
- esteatorreia
- esplenomegalia
- ascite
- encefalopatia
Fatores de risco
- sexo masculino
- doença inflamatória intestinal (DII)
- predisposição genética
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- fosfatase alcalina sérica
- gama-glutamiltransferase sérica
- aminotransferases séricas (aspartato aminotransferase, alanina aminotransferase)
- bilirrubina total sérica
- albumina sérica
- Hemograma completo
- tempo de protrombina
- ultrassonografia abdominal
- colangiopancreatografia por ressonância magnética (CPRM)
- imunoglobulina G4 (IgG4) sérica
Investigações a serem consideradas
- colangiopancreatografia retrógrada endoscópica (CPRE)
- IgM sérica
- anticorpo antinuclear
- anticorpo antimúsculo liso
- anticorpo antimitocondrial
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) abdominal
- biópsia hepática
- densitometria óssea
- colonoscopia
- exames não invasivos baseados em imagens para fibrose
Algoritmo de tratamento
doença inicial
doença hepática em estágio terminal
Colaboradores
Autores
S. Ian Gan, MD, FRCPC
Associate Clinical Professor
Vancouver General Hospital
University of British Columbia
Vancouver
BC
Declarações
SIG declares that he has no competing interests.
Nawaf Tareq Aboalfaraj, MBBS, FRCPC
Advanced Therapeutic Endoscopy Fellow
McGill University
Montreal
QC
Declarações
NTA declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr S. Ian Gan and Dr Nawaf Tareq Aboalfaraj would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Kris V. Kowdley and Dr Christine Schlenker, the previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
KVK is a member of the speakers bureau of Axcan Pharma, manufacturer of Urso250 and Urso Forte, and gives one or two lectures a year on treatment of cholestatic liver diseases. KVK has also received funding from the NIH for a research study of Urso in PSC. CS declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
LIsa Forman, MD
Professor of Medicine
University of Colorado
Aurora
CO
Declarações
LF declares that she has no competing interests.
James Neuberger, BM, BCh
Consultant Physician
Liver Unit
Queen Elizabeth Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Declarações
JN declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol. 2022 Sep;77(3):761-806.Texto completo Resumo
Bowlus CL, Arrivé L, Bergquist A, et al. AASLD practice guidance on primary sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2023 Feb 1;77(2):659-702.Texto completo
Chapman R, Fevery J, Kalloo A, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2010 Feb;51(2):660-78.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
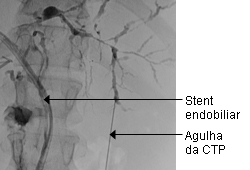
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Colangite esclerosante secundária
- Colangite relacionada à imunoglobulina G4 (IgG4)
- Hepatite autoimune
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- EASL clinical practice guidelines on liver transplantation
- ACR Appropriateness Criteria: abnormal liver function tests
Mais DiretrizesCalculadoras
Escore MELDNa (para fins de listagem de transplantes de fígado, não é adequado para pacientes com menos de 12 anos de idade ) (unidades SI)
Mais CalculadorasConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal