Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presença de fatores de risco
- poliúria
- polidipsia
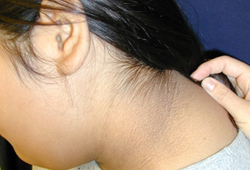
- acantose nigricans
- noctúria
Other diagnostic factors
- hipertensão
- infecções por levedura
- infecções cutâneas
- infecções do trato urinário
- fadiga
- visão turva
- perda de peso
Risk factors
- obesidade
- predisposição genética/história familiar
- origem étnica de alto risco
- puberdade
- sexo feminino
- ambiente diabético intrauterino
- pequeno para a idade gestacional
- crescimento rápido na primeira infância
- alimentação com mamadeira
- ingestão elevada de proteína na primeira infância
- ovários policísticos
- conteúdo lipídico intramiocelular
- deposição de gordura no fígado
- dificuldades de aprendizagem
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- tira reagente para exame de urina
- glicemia plasmática aleatória
- glicemia de jejum
- HbA1c
- autoanticorpos contra insulina, antígenos de ilhotas 2 (IA-2), descarboxilase do ácido glutâmico (DAG) e transportador de zinco 8 (ZnT8)
Tests to consider
- glicose plasmática de 2 horas
- peptídeo C aleatório
Treatment algorithm
cetoacidose ou estado hiperosmolar hiperglicêmico (EHH)
HbA1c <69 mmol/mol: sem acidose ou cetose
HbA1c ≥69 mmol/mol: sem acidose com ou sem cetose
Contributors
Authors
Jennifer Miller, MD

Professor
Department of Pediatrics
University of Florida
Gainesville
FL
Disclosures
JM declares that she has received research funding from Soleno Therapeutics, Harmony Biosciences, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. JM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Chelsea Zimmerman, MD
Clinical Physician
Pediatric Endocrinology
Endocrinology and Metabolism of East Alabama
Opelika
AL
Disclosures
CZ declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Jennifer Miller and Dr Chelsea Zimmerman would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Arlan Rosenbloom and Dr Paul Hiers, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
AR is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. Unfortunately, we have since been made aware that AR is deceased. PH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Philip Zeitler, MD, PhD
Professor of Pediatrics and Clinical Science
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Disclosures
PZ declares that he has no competing interests.
Julian P. Hamilton-Shield, MB, ChB, MD(Bristol), MRCP, FRCPCH, FRCPCH
Professor
Diabetes and Metabolic Endocrinology
School of Clinical Sciences
University of Bristol
UK
Disclosures
In the past, JPHS received speaking honoraria from Sanofi-Aventis, Roche, Abbott, Novo-Nordisk, and Nutricia. None of these talks were directly pertinent to the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Kristen Nadeau, MD
Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Aurora
CO
Disclosures
KN declares that she has no competing interests.
Dennis Styne, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Rumsey Chair of Pediatric Endocrinology
University of California
Sacramento
CA
Disclosures
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
Referências
Principais artigos
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes care. 2025 Jan;48(suppl 1):S1-352.Texto completo
Shah AS, Barrientos-Pérez M, Chang N, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2024: type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Horm Res Paediatr. 2024;97(6):555-83.Texto completo Resumo
Glaser N, Fritsch M, Priyambada L, et al. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2022: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022 Nov;23(7):835-56. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Intolerância à glicose
- Diabetes mellitus do tipo 1 (DMT1)
- Diabetes monogênico: diabetes juvenil de início na tardio (MODY)
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents
- Diabetes (type 1 and type 2) in children and young people: diagnosis and management
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Diabetes do tipo 2: devo tomar insulina?
Diabetes: o que posso fazer para me manter saudável?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal