Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presença de fatores de risco
- apresentação na primeira infância
Other diagnostic factors
- taquipneia/dispneia
- deficit no crescimento
- intolerância ao exercício
- pressão de pulso ampliada
- sopro contínuo do tipo mecânico/sopro de Gibson em lactentes nascidos a termo
- apneia
- pressão arterial (PA) diastólica baixa
- irritabilidade
- diaforese
- aumento dos sintomas respiratórios com infecção do trato respiratório superior
- sopro auscultado apenas durante a sístole
- precórdio hiperdinâmico
- frêmito sistólico
- terceira bulha cardíaca auscultada no ápice
- ruflar mesodiastólico no ápice
- pulsos periféricos amplos
- estertores pulmonares
Risk factors
- prematuridade
- rubéola materna
- sexo feminino
- síndrome do desconforto respiratório (SDR)
- altitudes elevadas
- história familiar
- raça negra
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- radiografia torácica
- eletrocardiograma (ECG)
- ecocardiograma
Investigations to consider
- cateterismo cardíaco e angiografia
Treatment algorithm
bebês prematuros com peso muito baixo ao nascer: terapia profilática
bebês prematuros (<32 semanas)
lactentes nascidos a termo e crianças: ductos pequenos a moderados
lactentes nascidos a termo e crianças: ductos grandes e/ou bebês sintomáticos muito pequenos para o fechamento com dispositivo
adultos
Contributors
Authors
Kenneth M. Coca, MD
Pediatric Cardiology Fellow
Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital
Saint Petersburg
FL
Disclosures
KMC declares that he has no competing interests.
Joyce T. Johnson, MD, MS
Director, Fetal Cardiology
Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital
Saint Petersburg
FL
Disclosures
JTJ declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Kenneth M. Coca and Dr Joyce T. Johnson would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Anji T. Yetman and Dr Nelangi M. Pinto, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
ATY declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Michael Cheung, BSc (Hons), MB ChB, MRCP, FRACP
Acting Head
Department of Cardiology
Royal Children's Hospital
Melbourne
Australia
Disclosures
MC declares that he has no competing interests.
Rajat Bhatt, MD
Assistant Professor
Internal Medicine
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC)
Lubbock
TX
Disclosures
RB declares that he has no competing interests.
Henry M. Sondheimer, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Clinical Director
Pediatric Cardiology
The Children's Hospital
Denver
CO
Disclosures
HMS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Baumgartner H, De Backer J, Babu-Narayan SV, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of adult congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 11;42(6):563-645.Full text
Hamrick SEG, Sallmon H, Rose AT, et al. Patent ductus arteriosus of the preterm infant. Pediatrics. 2020 Nov;146(5):e20201209.Full text Abstract
Wilson WR, Gewitz M, Lockhart PB, et al. Prevention of viridans group streptococcal infective endocarditis: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021 May 18;143(20):e963-78.Full text Abstract
John AS, Jackson JL, Moons P, et al. Advances in managing transition to adulthood for adolescents with congenital heart disease: a practical approach to transition program design: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Apr 5;11(7):e025278.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
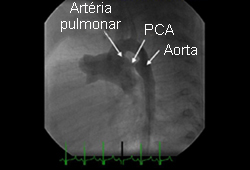
Differentials
- Zumbido venoso
- Fístula arterial coronariana
- Derivações no lado esquerdo (defeito do septo ventricular, defeito do septo atrioventricular)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines and recommendations for performance of the fetal echocardiogram
- Pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease: a scientific statement
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer