Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- nascimento de gêmeos
- posição supina para dormir e de repouso sem variação
- diminuição do tempo na posição pronada durante a vigília
- inclinação da cabeça
- cabeça virada com rotação ativa reduzida para o lado afetado
- endireitamento da cabeça reduzido para o lado contralateral
- massa no esternocleidomastoideo
- elevação do ombro ipsilateral
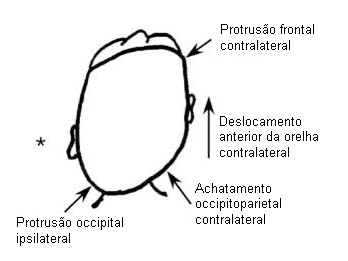
- plagiocefalia/assimetria craniofacial
- hipertropia no lado contralateral
- clique ou assimetria do quadril
Fatores de risco
- plagiocefalia
- parto pélvico
- parto cesáreo
- gêmeo A (na parte mais inferior do útero)
- partos complicados (fórceps ou vácuo)
- trauma no nascimento
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- raio-X da coluna cervical
- radiografia pélvica
- ultrassonografia do quadril
Investigações a serem consideradas
- ultrassonografia do pescoço
- radiografia do crânio
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) cervical/do crânio
Algoritmo de tratamento
controle da cabeça inadequado ou idade <5 meses
bom controle da cabeça e idade >5 meses
Colaboradores
Autores
Joyce L. Oleszek, MD

Associate Professor
Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
University of Colorado School of Medicine and The Children's Hospital Colorado
Aurora
CO
Declarações
JLO is co-author of one of the references cited in this topic.
Revisores
Elizabeth A. Moberg-Wolff, MD
Associate Professor
Program Director
Tone Management and Mobility
Children's Hospital of Wisconsin
Milwaukee
WI
Declarações
EAMW declares that she has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Cheng JC, Wong MW, Tang SP, et al. Clinical determinants of the outcome of manual stretching in the treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants. A prospective study of eight hundred and twenty-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(5):679-87. Resumo
Cheng JC, Au AW. Infantile torticollis: a review of 624 cases. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994;14:802-808. Resumo
Binder H, Eng GD, Gaiser JF, et al. Congenital muscular torticollis: results of conservative management with long-term follow-up in 85 cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987 Apr;68(4):222-5. Resumo
Positioning and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS): update. American Academy of Pediatrics Task Force on Infant Positioning and SIDS. Pediatrics. 1996;98:1216-1218. Resumo
Emery C. The determinants of treatment duration for congenital muscular torticollis. Phys Ther. 1994 Oct;74(10):921-9.Texto completo Resumo
Cheng JC, Tang SP, Chen TM, et al. The clinical presentation and outcome of treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants - a study of 1,086 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 2000 Jul;35(7):1091-6. Resumo
Cheng JC, Tang SP. Outcome of surgical treatment of congenital muscular torticollis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999 May;(362):190-200. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Paralisia do músculo oblíquo superior
- Tumor do sistema nervoso central
- Anomalia vertebral
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Physical therapy management of congenital muscular torticollis
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal