Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- perda auditiva assimétrica
- episódios progressivos de tontura
- zumbido
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- dificuldade em localizar sons
- cefaleia
- dormência facial
- fraqueza facial
- diplopia no olhar lateral
- nistagmo
- perda de equilíbrio e dificuldades de coordenação
- piscar mais lento
- dificuldades de deglutição
- distúrbios da marcha
- hidrocefalia
- papiledema
- pressão intracraniana elevada
Fatores de risco
- schwannomatose relacionada a neurofibromatose
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- audiograma
- RNM ponderada em T1 usando contraste à base de gadolínio
- TC de crânio com contraste
Investigações a serem consideradas
- reflexos auditivos do tronco encefálico
Algoritmo de tratamento
tumor pequeno (graus 1-2 de Koos)
tumor médio (graus 3-4 de Koos, tamanho do tumor <3 cm)
tumor grande (graus 4 de Koos, tamanho do tumor >3 cm)
Colaboradores
Autores
Michael J. Link, MD
Professor
Departments of Neurologic Surgery and Otorhinolaryngology
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
MJL is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Matthew L. Carlson, MD
Professor
Departments of Neurologic Surgery and Otorhinolaryngology
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
MLC is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Michael J. Link and Dr Matthew L. Carlson would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ryojo Akagami, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
RA has been reimbursed for instructing at a dissection course by Stryker and gives yearly lectures at a Canadian resident review course. RA was an expert panellist at a session on vestibular schwannomas at the 2019 NASBS meeting.
Peer reviewers
Rick Friedman, MD, PhD
Professor of Otolaryngology and Neurosurgery
UC San Diego
La Jolla
CA
Disclosures
RF declares that he has no competing interests.
Iain Swan, MD, FRCS
Senior Lecturer in Otolaryngology
Honorary Consultant Otolaryngologist
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
IS declares that he has no competing interests.
Patrice Tran Ba Huy, MD
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
AP-HP
Hopital Lariboisiere
Service ORL
Universite Paris 7
Paris and Laboratoire des Réseaux Sensorimoteurs
Paris
France
Disclosures
PTBH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Goldbrunner R, Weller M, Regis J, et al. EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol. 2020 Jan 11;22(1):31-45.Full text Abstract
Ren Y, Chari DA, Vasilijic S, et al. New developments in neurofibromatosis type 2 and vestibular schwannoma. Neurooncol Adv. 2021 Jan-Dec;3(1):vdaa153.Full text Abstract
Lin VY, Stewart C, Grebenyuk J, et al. Unilateral acoustic neuromas: long-term hearing results in patients managed with fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy, hearing preservation surgery, and expectantly. Laryngoscope. 2005 Feb;115(2):292-6. Abstract
Pollock BE. Management of vestibular schwannomas that enlarge after stereotactic radiosurgery: treatment recommendations based on a 15 year experience. Neurosurgery. 2006 Feb;58(2):241-8. Abstract
Darrouzet V, Martel J, Enee V, et al. Vestibular schwannoma surgery outcomes: our multidisciplinary experience in 400 cases over 17 years. Laryngoscope. 2004 Apr;114(4):681-8. Abstract
Roland JT Jr, Fishman AJ, Golfinos JG, et al. Cranial nerve preservation in surgery for large acoustic neuromas. Skull Base. 2004 May;14(2):85-91.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
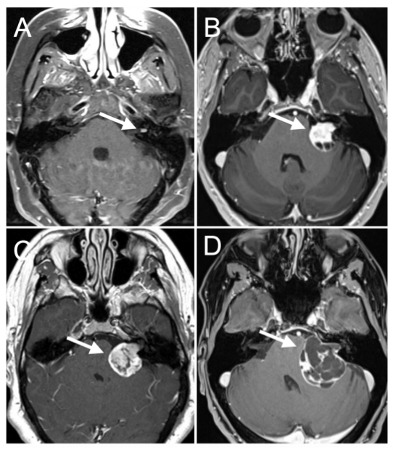
Differentials
- Meningioma
- Cisto epidermoide
- Schwannoma do nervo facial
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Suspected cancer: recognition and referral
- EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma
More GuidelinesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Zumbido
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal