Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- posições de provocação específicas
- duração rápida da vertigem
- vertigem episódica
- episódios intensos de vertigem
- início súbito de vertigem
- náuseas, desequilíbrio e tontura
- ausência de sintomas neurológicos ou otológicos associados
- exame neurológico normal
- manobra de Dix-Hallpike positiva ou rotação de cabeça lateral supina positiva
- exame otológico normal
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- idade >50 anos
- sexo feminino
- vertigem posicional na ausência de nistagmo
Fatores de risco
- idade mais avançada
- sexo feminino
- trauma cranioencefálico
- neurite vestibular
- labirintite
- enxaquecas
- cirurgia da orelha interna
- Doença de Ménière
- otite média
- hipertensão
- hiperlipidemia
- diabetes mellitus
- insuficiência vertebrobasilar
- arterite de células gigantes
- osteoporose
- intubação
- posicionamento lateral de cabeça habitual durante o repouso no leito (VPPB ipsilateral)
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- Manobra de Dix-Hallpike
- rotações de cabeça lateral na posição supina
Investigações a serem consideradas
- audiograma
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) cranioencefálica
Algoritmo de tratamento
apresentação inicial
manobras de reposicionamento múltiplas e exercícios de reabilitação vestibular inefetivos
Colaboradores
Autores
Lorne S. Parnes, MD, FRCSC

Professor
Departments of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Clinical Neurological Sciences
University of Western Ontario
London
Canada
Declarações
LSP is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Shahin Nabi, MD, FRCSC

Departments of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery and Clinical Neurological Sciences
University of Western Ontario
London
Canada
Declarações
SN declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Joel Goebel, MD, FACS
Professor and Vice Chairman
Residency Program Director
Dizziness and Balance Center Director
Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Declarações
JG is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Stephen P. Cass, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Otolaryngology
University of Colorado
Aurora
CO
Declarações
SPC is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Steven D. Rauch, MD
Associate Professor of Otology and Laryngology
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Declarações
SDR declares that he has no competing interests.
Malcolm Hilton, BA, BMBCh, FRCS (Eng), FRCS (ORL-HNS)
Consultant Otolaryngologist & Honorary Lecturer
Royal Devon & Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
Exeter
UK
Declarações
MH is the author of one reference cited in this topic.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Hilton MP, Pinder DK. The Epley (canalith repositioning) manoeuvre for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Dec 8;(12):CD003162.Texto completo Resumo
Leveque M, Labrousse M, Seidermann L, et al. Surgical therapy in intractable benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007 May;136(5):693-8. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
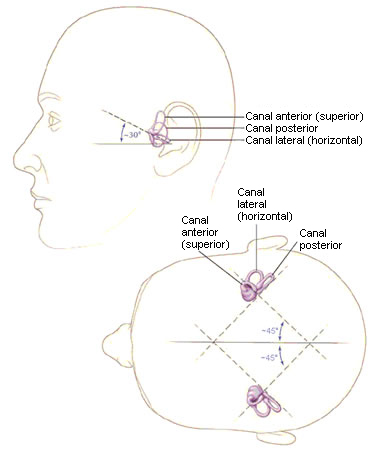
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Doença de Ménière
- Neuronite vestibular
- Labirintite
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- ACR appropriateness criteria: dizziness and ataxia
- Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (update)
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Vertigem posicional paroxística benigna
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal