Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- vertigem
- tontura
- náuseas e vômitos
- perda auditiva
- nistagmo
- zumbido
- otorreia
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- movimentos rápidos da cabeça ou do corpo relacionados à vertigem
- sintomas tipo influenza
- otalgia
Fatores de risco
- infecções virais
- otite média crônica supurativa
- otite média aguda
- colesteatoma
- meningite
- malformações da orelha interna
- doenças autoimunes da orelha
- sífilis
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- audiograma
- teste de Weber
- teste de Rinne
Investigações a serem consideradas
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) ou ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) cranioencefálica
- videonistagmografia (VNG)
- teste do impulso da cabeça (HIT) e teste do impulso da cabeça por vídeo (vHIT)
- teste da cadeira rotatória
- potencial evocado miogênico vestibular (PEMV)
- sorologia para sífilis
- coloração de Gram e cultura do líquido cefalorraquidiano
- teste rápido para sorologia de HIV
- perfil metabólico básico (incluindo ureia e creatinina)
Algoritmo de tratamento
labirintite
Neurite vestibular
com sintomas vestibulares persistentes pós-tratamento
Colaboradores
Autores
Tiffany Peng Hwa, MD
Assistant Professor
Medical Director, Center for Adult Onset-Hearing Loss
Director, Temporal Bone Surgical Dissection Laboratory
Division of Otology & Neurotology
Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
University of Pennsylvania Health System
Philadelphia
PA
Declarações
TPH has received honoraria from Amgen/Horizon Therapeutics for participation on the advisory board for ototoxicity and the agent, teprotumumab. TPH has given numerous educational lectures to trainees for non-pay, not specifically focused on labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis. MedEl has reimbursed TPH for attendance at a cochlear implant training workshop regarding their new anatomy-based fitting technology. TPH has a pending NIH grant application regarding central auditory processing and speech perception assessment that has no relationship to labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis. TPH has an investigator-initiated research grant from Cochlear Corporation, also unrelated to labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis.
Agradecimentos
Dr Tiffany Peng Hwa would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Brandon Isaacson, the previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
BI is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Revisores
Lawrence R. Lustig, MD
BMJ Best Practice ENT expert panel member
Professor and Chair
Department of Otolaryngology
Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
New York
NY
Declarações
LRL declares that he has no competing interests.
Desi Schoo, MD
Assistant Professor of Otology, Neurotology, and Cranial Base Surgery
Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus
OH
Declarações
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Iain Swan, MD, FRCS
Senior Lecturer in Otolaryngology
Honorary Consultant Otolaryngologist
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Glasgow
UK
Declarações
IS declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Strupp M, Bisdorff A, Furman J, et al. Acute unilateral vestibulopathy/vestibular neuritis: Diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res. 2022 Jun 11;32(5):389-406.Texto completo Resumo
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Hearing loss in adults: assessment and management. Oct 2023 [internet publication].Texto completo
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Aug;161(suppl 1):S1-45.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
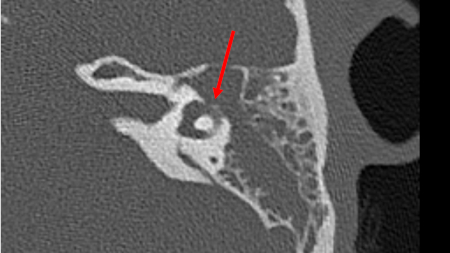
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Doença de Ménière
- Acidente vascular cerebral na fossa posterior
- Fratura do osso temporal
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Hearing loss in adults: assessment and management
- Suspected neurological conditions: recognition and referral
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Labirintite e neurite vestibular
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Como examinar a orelha
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal