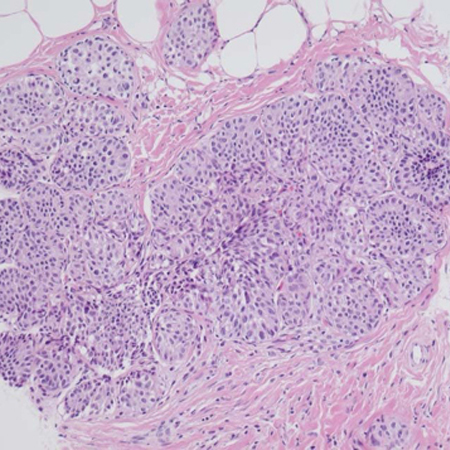
Summary
Definition
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- história familiar de câncer de mama
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- descarga mamilar
- nódulo mamário
- erupção cutânea, semelhante a eczema, no mamilo
- ulceração
Fatores de risco
- história familiar de câncer de mama
- doença mamária benigna em biópsia anterior
- síndrome do câncer de mama e ovário hereditário (CMOH)
- síndrome de Li-Fraumeni
- Síndrome de Cowden
- câncer gástrico difuso hereditário (CGDH)
- síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers
- Síndrome de Klinefelter
- idade avançada na menopausa
- idade avançada na primeira gestação a termo
- nuliparidade
- pouca atividade física
- ingestão elevada de vitamina A
- ataxia-telangiectasia
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- mamografia
Investigações a serem consideradas
- biópsia percutânea com agulha grossa
- biópsia excisional
- biópsia do linfonodo sentinela (BLS)
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) da mama
- ultrassonografia das mamas
- perfil de receptores hormonais
- avaliação genética
Algoritmo de tratamento
mulheres com carcinoma ductal in situ (CDIS) de baixo risco
mulheres com CDIS de alto risco; todas as mulheres com CDIS
Carcinoma lobular in situ (CLIS)
recidiva local do CDIS
Colaboradores
Autores
Edward R. Sauter, MD, PhD

Medical Officer
Breast and Gynecologic Cancer Working Group
Division of Cancer Prevention
National Cancer Institute
Bethesda
MD
Declarações
ERS is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Agradecimentos
Dr Edward R. Sauter would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rachel L. Ruhlen, a previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
RLR declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores
Carla Boetes, MD, PhD
Radiologist
Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre
Nijmegen
The Netherlands
Declarações
CB is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Alessandra Balduzzi, MD
Assistant in the Division of Medical Oncology
European Institute of Oncology
Milan
Italy
Declarações
AB declares that she has no competing interests.
Kala Visvanathan, MBBS, FRACP, MHS
Associate Professor in Epidemiology and Medical Oncology
Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and Bloomberg School of Public Health
Baltimore
MD
Declarações
KV is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Glyn T. Neades, MB ChB, FRCS(Glas), FRCS(Ed), ChM
Consultant Surgeon and Honorary Senior Lecturer
Edinburgh Breast Unit
Western General Hospital
Edinburgh
UK
Disclosures
GTN is a principal investigator for the IBIS-II trial, and is an author of a guideline cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer risk reduction [internet publication].Full text
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer [internet publication].Full text
Loibl S, André F, Bachelot T, et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2024 Feb;35(2):159-82.Full text
Morrow M, Van Zee KJ, Solin LJ, et al. Society of Surgical Oncology-American Society for Radiation Oncology-American Society of Clinical Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Nov 20;34(33):4040-6. [Reaffirmed 2019.]Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
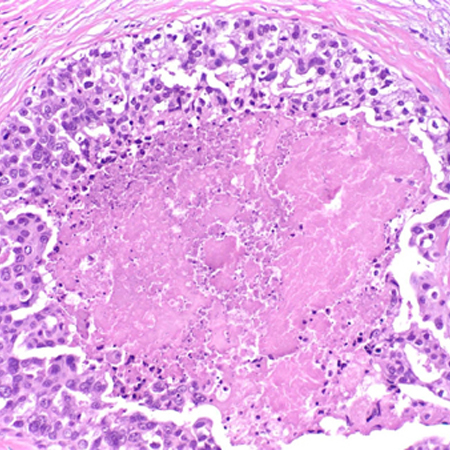
Differentials
- Câncer de mama invasivo
- Hiperplasia atípica
- Fibroadenoma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Suspected cancer: recognition and referral
- ACR appropriateness criteria: breast implant evaluation
More GuidelinesPatient information
Câncer de mama localmente avançado: o que é?
Câncer de mama: rastreamento de rotina (mamografia)
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer