Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- pródromo inespecífico
- sintomas neurológicos graves (coma, anormalidades focais, convulsões)
- sintomas neurológicos leves (cefaleia, confusão)
- febre
Other diagnostic factors
- idade entre 30 e 50 anos
- sintomas digestivos (náuseas, vômitos, diarreia, dor abdominal)
- fraqueza
- sintomas de sangramento (púrpura, equimoses, menorragia)
Risk factors
- etnia negra
- sexo feminino
- obesidade
- gestação (parto próximo ou período pós-parto)
- terapias para câncer
- Infecção pelo vírus da imunodeficiência humana (HIV)
- transplante de medula óssea
- agentes antiplaquetários
- quinina
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- contagem plaquetária
- hemoglobina
- haptoglobina
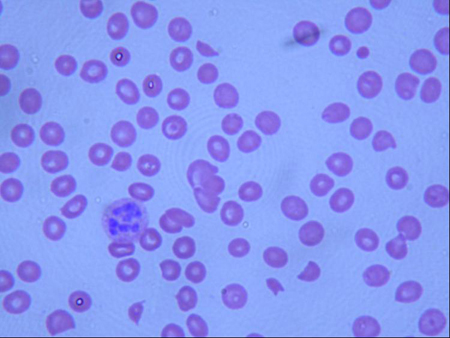
- esfregaço de sangue periférico
- contagem de reticulócitos
- urinálise
- ureia e creatinina
- teste de Coombs direto
Tests to consider
- ensaios da atividade da enzima ADAMTS-13 e títulos dos inibidores
Treatment algorithm
PTT adquirida (idiopática): episódio agudo
PTT adquirida (idiopática): após a resolução de episódio agudo
Contributors
Authors
Sandeep K. Rajan, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology
Vanderbilt University
Nashville
Tennessee
Disclosures
SKR has received honoraria for advisory consultancy and speakers bureau, and received research funds from Alexion, Novo-Nordisk, Sanofi and Appelis.
Acknowledgements
Dr Sandeep K. Rajan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rebecca Fischer Connor, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
RFC declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
James N. George, MD
George Lynn Cross Professor
Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City
OK
Disclosures
JNG declares that he has no competing interests.
Christoph Pechlaner, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Department of Internal Medicine
Innsbruck Medical University
Innsbruck
Austria
Disclosures
CP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Scully M, Cataland S, Coppo P, et al. Consensus on the standardization of terminology in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related thrombotic microangiopathies. J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Feb;15(2):312-22.Full text Abstract
Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012 Aug;158(3):323-35.Full text Abstract
Terrell DR, Williams LA, Vesely SK, et al. The incidence of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: all patients, idiopathic patients, and patients with severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jul;3(7):1432-6.Full text Abstract
Moschowitz E. An acute febrile pleiochromic anemia with hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries. Arch Intern Med. 1925;36:89.
Moore JC, Hayward CP, Warkentin TE, et al. Decreased von Willebrand factor protease activity associated with thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood. 2001 Sep 15;98(6):1842-6.Full text Abstract
Banno F, Kokame K, Okuda T, et al. Complete deficiency in ADAMTS13 is prothrombotic, but it alone is not sufficient to cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2006 Apr 15;107(8):3161-6.Full text Abstract
Veyradier A, Meyer D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and its diagnosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Nov;3(11):2420-7. Abstract
Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, et al. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 8;325(6):393-7. Abstract
Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021 Apr 8;137(14):1855-61.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Síndrome hemolítico-urêmica (SHU)
- Síndrome hemolítico-urêmica atípica (SHUa)
- Hipertensão maligna
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer