Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presença de fatores de risco
- história de infecções prévias
- dispneia
- dor perianal
- dor no flanco
- lesões vermelhas da pele
- exames torácicos anormais
- calafrios
- febre
- linfadenopatia crônica
- baixo crescimento
- dor nas articulações
- dor facial
- lesões coriorretinianas
- cicatrização desfigurante da pele
Other diagnostic factors
- fadiga
- diarreia
- dor abdominal
- tosse
- anorexia
- artralgias
- náuseas e vômitos
- hematúria
- fluxo urinário anormal
- hepatoesplenomegalia
- história familiar de lúpus discoide
- úlcera oral
- erupção cutânea
Risk factors
- história familiar de doença granulomatosa crônica
- idade <5 anos
- sexo masculino
- inativação anormalmente distorcida do cromossomo X nos portadores da forma ligada ao cromossomo X
- polimorfismos da mieloperoxidase e dos FCgammaRIIIb
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- Hemograma completo
- Velocidade de hemossedimentação (VHS)
- proteína C-reativa
- calprotectina fecal
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) do tórax
- TC ou ultrassonografia para infecção ativa
- tomografia por emissão de pósitrons (PET) com fluordesoxiglucose (FDG) F-18 de corpo inteiro
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM)
- colonoscopia
- testes de função pulmonar
- teste do nitroazul de tetrazólio (NBT)
- teste da di-hidrorodamina (DHR) 123
Tests to consider
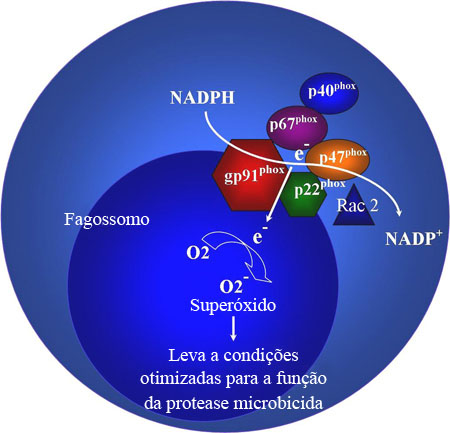
- sequenciamento genético para os genes codificando os componentes da nicotinamida adenina dinucleotídeo fosfato-oxidase (NADPH oxidase)
- Western blotting
- análise da citometria de fluxo dos componentes individuais da NADPH oxidase
Treatment algorithm
infecção ativa sem risco de vida: na primeira apresentação
infecção ativa com risco de vida: na primeira apresentação
após o tratamento empírico inicial
após resolução de episódio agudo
Contributors
Authors
David Lowe, MA, MB Bchir, PhD, FRCP
Consultant Clinical Immunologist
The Royal Free Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
DL has received personal fees from Gilead for an educational video and from Merck for a roundtable discussion. He has received speaker fees from Biotest, Takeda, and Astra-Zeneca and support to attend a conference from Octapharma. DL also holds research grants from NIHR, MRC, LifeArc, GSK, and Bristol Myers Squibb and has received consultancy fees from GSK paid to his institution.
Acknowledgements
Dr David Lowe would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Adrian Thrasher, Dr Rebecca A. Marsh, and Dr Jack J. Bleesing, previous contributors to this topic. AT is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. RAM and JJB declare that they have no competing interests. Dr Rebecca A. Marsh and Dr Jack J. Bleesing wish to thank Dan Marmer, Carrie Koenig, and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Clinical Diagnostic Immunology Lab. They also wish to thank Steven M. Holland, MD, Thomas Fleisher, MD, and Anthony Segal, MD, PhD, for helpful correspondence.
Peer reviewers
Niraj C. Patel, MD, MS
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Duke University
Durham
NC
Disclosures
NCP is on the Speakers Bureau for Amgen.
Andrew Gennery, MD
Reader in Paediatric Immunology & HSCT
Institute of Cellular Medicine
Medical School
Newcastle University
Newcastle-upon-Tyne
UK
Disclosures
AG is an author of a reference cited in this topic. AG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Thomsen IP, Smith MA, Holland SM, et al. A comprehensive approach to the management of children and adults with chronic granulomatous disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016 Nov-Dec;4(6):1082-8. Abstract
Bonilla FA, Khan DA, Ballas ZK, et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Nov;136(5):1186-205.e1-78.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- deficiência da adesão leucocitária tipo I
- deficiência de glicose-6-fosfato desidrogenase
- deficiência de mieloperoxidase
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Chronic granulomatous disorder: a guide for medical professionals
- Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency
More GuidelinesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal