Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- fenda labial bilateral ± palatina
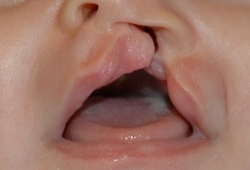
- fenda labial unilateral ± palatina
- fenda palatina isolada
- microforma de fenda labial
- fenda palatina submucosa isolada
- ultrassonografia pré-natal positiva
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- dificuldade para se alimentar
- baixo ganho de peso
- obstrução das vias aéreas
Fatores de risco
- predisposição genética
- medicamentos anticonvulsivantes
- tabagismo materno
- consumo materno de bebidas alcoólicas
- deficiência de ácido fólico
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- audiograma
- consulta genética
Investigações a serem consideradas
- exame de resposta auditiva evocada do tronco encefálico (BERA)
- raio-x da coluna vertebral
- ultrassonografia renal
- hibridização in situ fluorescente (FISH)
- exame oftalmológico
Algoritmo de tratamento
fenda labial e fenda palatina completas
fenda palatina isolada
fenda labial isolada
Colaboradores
Autores
Travis T. Tollefson, MD, MPH, FACS

Professor and Director
Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
Cleft and Craniofacial Team
University of California Davis
Sacramento
CA
Declarações
TTT has received an honorarium and reimbursement for travel by the AO Foundation for teaching on a facial trauma course. TTT serves on the American Board of Otolaryngology and the American Board of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, and receives a royalty from Thieme publishing for the textbook Complete Cleft Care. TTT is an author of studies referenced in this topic. TTT serves as editor-in-chief of the journal ‘Facial Plastic Surgery and Aesthetic Medicine’.
David A. Shaye, MD

Instructor
Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Massachusetts Eye and Ear
Harvard University
Boston
MA
Declarações
DAS has received an honorarium and reimbursement for travel by the AO Foundation for teaching on a facial trauma course.
Revisores
Jordan N. Halsey, MD
Pediatric Plastic and Craniofacial Surgeon
Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery
Johns Hopkins University
Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery
University of South Florida
Tampa
FL
Declarações
JNH declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Veau V. Bec-de-lièvre; formes cliniques - chirurgie. Avec la collaboration de J Récamier. Paris, France: Masson et Cie; 1938.
Wyszynski DF, Beaty TH, Maestri NE. Genetics of nonsyndromic oral clefts revisited. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1996 Sep;33(5):406-17.Texto completo Resumo
Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. Palate examination: identification of cleft palate in the newborn. Oct 2014 [internet publication].Texto completo
American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association. Parameters for evaluation and treatment of patients with cleft lip/palate or other craniofacial differences. Jan 2018 [internet publication].Texto completo
Boyce JO, Reilly S, Skeat J, et al. ABM Clinical Protocol #17: Guidelines for breastfeeding infants with cleft lip, cleft palate, or cleft lip and palate-revised 2019. Breastfeed Med. 2019 Sep;14(7):437-44.Texto completo Resumo
Cutting C, Grayson B, Brecht L, et al. Presurgical columellar elongation and primary retrograde nasal reconstruction in one-stage bilateral cleft lip and nose repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012 Sep;130(3):659-66. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diretrizes
- Parameters for evaluation and treatment of patients with cleft lip/palate or other craniofacial differences
- Palate examination: identification of cleft palate in the newborn
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal