Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- dor ao deglutir
- febre (>38 °C [>100.5 °F])
- exsudato tonsilar
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- início súbito de faringite
- cefaleia
- dor abdominal
- náuseas e vômitos
- presença de tosse ou coriza
- eritema tonsilar
- aumento tonsilar
- aumento dos linfonodos cervicais anteriores
Fatores de risco
- idade entre 5 e 15 anos
- contato com pessoas infectadas em ambientes fechados (por exemplo, creche, escola, prisão)
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- cultura faríngea
- teste rápido de detecção do antígeno estreptocócico
Tests to consider
- teste sorológico para estreptococos
- contagem leucocitária total e diferencial
- anticorpos heterófilos
- culturas vaginais e cervicais (ou penianas) e retais
- teste da carga viral do vírus da imunodeficiência humana (HIV)
- radiografia cervical de vista lateral, com exposição dos tecidos moles
Treatment algorithm
amigdalite aguda não causada por infecção por estreptococos beta-hemolíticos do grupo A
amigdalite aguda causada por infecção por estreptococos beta-hemolíticos do grupo A
episódios recorrentes de amigdalite
Contributors
Authors
Christos Georgalas, PhD, DLO, FRCS (ORL-HNS)

Professor of Surgery - Head and Neck
University of Nicosia
Cyprus
Disclosures
CG declares that he has no competing interests.
Eleftherios Margaritis, PhD, MSc, MD

Otolaryngologist - Head and Neck Surgeon
Collaborator in Otolaryngology
ENT Department
Hippokration University Hospital
Athens
Greece
Disclosures
EM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Itzhak Brook, MD, MSc
Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine
Georgetown University
Washington
DC
Disclosures
IB declares that he has no competing interests.
Chris Del Mar, MB BChir, FRACGP MD, MA, FAFPHM
Dean
Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine
Bond University
Gold Coast
Queensland
Australia
Disclosures
CDM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Shaikh N, Swaminathan N, Hooper EG, et al. Accuracy and precision of the signs and symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis in children: a systematic review. J Pediatr. 2012 Mar;160(3):487-93. Abstract
Aalbers J, O'Brien KK, Chan WS, et al. Predicting streptococcal pharyngitis in adults in primary care: a systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of symptoms and signs and validation of the Centor score. BMC Med. 2011 Jun 1;9:67.Full text Abstract
Spinks A, Glasziou PP, Del Mar CB. Antibiotics for sore throat. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 5;(11):CD000023.Full text Abstract
Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102.Full text Abstract
de Cassan S, Thompson MJ, Perera R, et al. Corticosteroids as standalone or add-on treatment for sore throat. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 1;5(5):CD008268.Full text Abstract
Burton MJ, Glasziou PP, Chong LY, et al. Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical treatment for chronic/recurrent acute tonsillitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 19;(11):CD001802.Full text Abstract
Windfuhr JP, Toepfner N, Steffen G, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tonsillitis II. Surgical management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Apr;273(4):989-1009. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
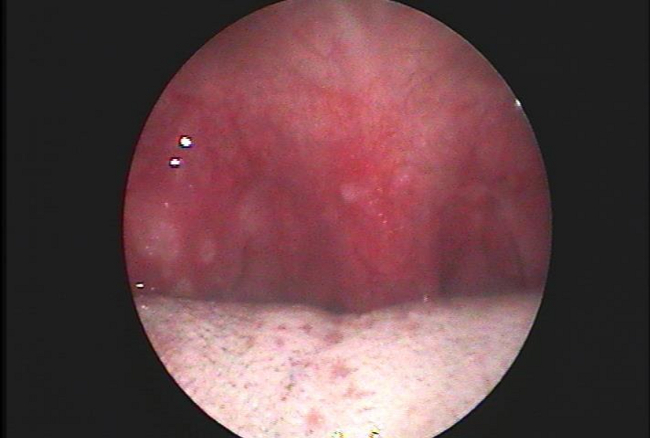
Differentials
- Mononucleose infecciosa
- Epiglotite
- Abscesso peritonsilar (esquinência)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Clinical practice guideline: tonsillectomy in children (update)
- Sore throat (acute): antimicrobial prescribing
More GuidelinesPatient information
Tonsilectomia (cirurgia para remover as amígdalas)
Faringite
More Patient informationCalculators
Critérios de Avaliação e Tratamento da Faringite (McIsaac)
More CalculatorsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer