Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- úlceras orais
- paciente afebril
- ausência de ulceração genital ou ocular
- sem história de imunodeficiência
- ausência de palidez
Fatores de risco
- história familiar positiva
- não fumante ou abandono do hábito de fumar
- trauma
- idade <30 anos
- crianças alimentadas com leite de vaca
- sexo feminino
- altos níveis de estresse
- intolerância alimentar
- desequilíbrio hormonal
- uso de creme dental contendo lauril sulfato de sódio
Investigações diagnósticas
Investigações a serem consideradas
- Hemograma completo
- ferritina sérica
- folato sérico
- vitamina B12 sérica
- imunoglobulina A-transglutaminase tecidual (IgA-tTG) sérica
- sorologia viral (por exemplo, HIV ou vírus Epstein-Barr)
- velocidade de hemossedimentação e proteína C-reativa
- biópsia
- teste de fator antinuclear
- teste sorológico para HIV
Algoritmo de tratamento
todos os pacientes
Colaboradores
Autores
Jennifer Taylor, BDS, MFDS RCS, MBChB FDS (OM), PhD
Consultant and Honorary Senior Lecturer in Oral Medicine
Glasgow Dental Hospital and School
Glasgow
Scotland
UK
Declarações
JT declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the late Professor Crispian Scully for his contribution to this topic.
Revisores
James J. Sciubba, DMD, PhD
Consultant for Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine
The Milton J. Dance Head and Neck Center
Greater Baltimore Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Declarações
JJS declares that he has no competing interests.
Pepe Shirlaw, BDS, FDS RCPS
Consultant in Oral Medicine
Guy’s Hospital
Great Maze Pond
London
UK
Declarações
PS declares that she has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Scully C. Clinical practice. Aphthous ulceration. N Engl J Med. 2006 Jul 13;355(2):165-72. Resumo
Scully C, Gorsky M, Lozada-Nur F. The diagnosis and management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a consensus approach. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003 Feb;134(2):200-7. Resumo
Brocklehurst P, Tickle M, Glenny AM, et al. Systemic interventions for recurrent aphthous stomatitis (mouth ulcers). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD005411.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
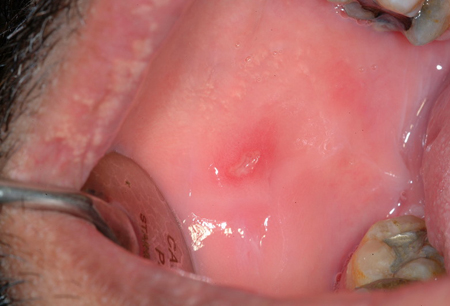
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Síndrome de Behçet
- Úlcera maligna
- Deficiência de folato
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- The diagnosis and management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a consensus approach
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Úlceras orais
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal