Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- tosse intratável
- febre
- dispneia
- sibilância
- estertores
Fatores de risco
- nível de consciência reduzido (escore na escala de coma de Glasgow <9)
- doença mais grave
- anestesia geral
- idade >70 anos
- sexo masculino
- trauma cranioencefálico
- doença cerebrovascular
- tubo endotraqueal ou de traqueostomia
- disfagia
- dificuldades nas vias aéreas
- refeição de bário
- doença do refluxo gastroesofágico
- tubos de alimentação
- posição supina
- retardo do esvaziamento gástrico
- obesidade
- medicamentos que reduzem o tônus dos esfíncteres esofágicos
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- radiografia torácica
Investigações a serem consideradas
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) do tórax
- broncoscopia com lavagem broncoalveolar
- Hemograma completo
- gasometria arterial
Algoritmo de tratamento
pneumonite causada por aspiração de conteúdo gástrico
pneumonite devida à aspiração de bário
pneumonite sem resolução após 48 horas
Colaboradores
Autores
Madison Macht, MD
Volunteer Clinical Faculty
Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine
University of Colorado Denver
Aurora
CO
Declarações
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Madison Macht would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Kamran Mahmood, Dr Scott Shofer, Dr Septimiu Murgu, and Dr Henri Colt, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
KM, SS, SM, and HC declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Andrew Parfitt, MBBS, FFAEM
Clinical Director
Acute Medicine
Associate Medical Director
Consultant Emergency Medicine
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
Clinical Lead and Consultant
Accident and Emergency Medicine
St Thomas' Hospital
London
UK
Declarações
AP declares that he has no competing interests.
Momen M. Wahidi, MD, MBA
Director
Interventional Pulmonology
Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Duke University Medical Center
Durham
NC
Declarações
MMW declares that he has no competing interests.
Referências
Principais artigos
Marik PE. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 1;344(9):665-71. Resumo
Ng A, Smith G. Gastroesophageal reflux and aspiration of gastric contents in anesthetic practice. Anesth Analg. 2001 Aug;93(2):494-513.Texto completo Resumo
Metheny NA, Clouse RE, Chang YH, et al. Tracheobronchial aspiration of gastric contents in critically ill tube-fed patients: frequency, outcomes, and risk factors. Crit Care Med. 2006 Apr;34(4):1007-15.Texto completo Resumo
Smith Hammond CA, Goldstein LB. Cough and aspiration of food and liquids due to oral-pharyngeal dysphagia: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2006 Jan;129(1 suppl):154S-68S.Texto completo Resumo
Boyd M, Chatterjee A, Chiles C, et al. Tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration in adults. South Med J. 2009 Feb;102(2):171-4. Resumo
Paintal HS, Kuschner WG. Aspiration syndromes: 10 clinical pearls every physician should know. Int J Clin Pract. 2007 May;61(5):846-52. Resumo
Practice guidelines for preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration: Application to healthy patients undergoing elective procedures: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration. Anesthesiology. 2017 Mar;126(3):376-93.Texto completo Resumo
Smith I, Kranke P, Murat I, et al. Perioperative fasting in adults and children: guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2011 Aug;28(8):556-69.Texto completo Resumo
Australian and New Zealand Society for Geriatric Medicine. Australian and New Zealand Society for Geriatric Medicine. Position statement - dysphagia and aspiration in older people. Australas J Ageing. 2011 Jun;30(2):98-103. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
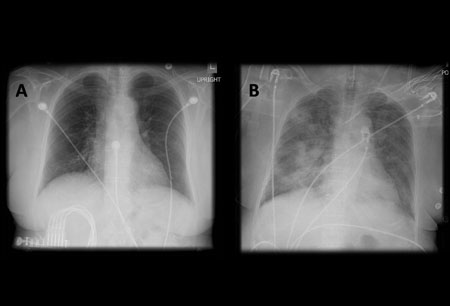
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Síndrome do desconforto respiratório agudo
- Exacerbação da asma
- Fibrose cística com exacerbação
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: an official clinical practice guideline
- ACR appropriateness criteria: dysphagia
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal