Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- história familiar de DPO
- assintomático
Outros fatores diagnósticos
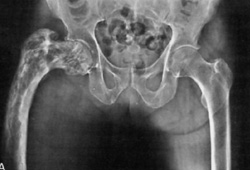
- comprometimento do fêmur, da pelve e/ou do crânio
- dor no osso longo ou dorsalgia
- fratura patológica
- deformidades ósseas (por exemplo, bossa frontal, prognatismo, arqueamento ósseo)
- temperatura local elevada
- perda auditiva
- dor facial
- dentes frouxos ou distúrbio da mastigação
- fosfatase alcalina elevada isolada
Fatores de risco
- história familiar de DPO
- idade >50 anos
- sexo masculino (faixa etária dos 45 a 74 anos)
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- radiografia simples
- cintilografia óssea
- fosfatase alcalina sérica total
- fosfatase alcalina ósseo-específica
- cálcio sérico
- peptídeo N-terminal do procolágeno sérico 1 (P1NP)
- propeptídeo C-terminal sérico do colágeno do tipo1 (CTX)
- testes da função hepática
- 25-hidroxivitamina D sérica
Investigações a serem consideradas
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) ou ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM)
- biópsia dos ossos
Algoritmo de tratamento
pacientes assintomáticos, diagnóstico incidental
pacientes sintomáticos
Colaboradores
Autores
Roberto Civitelli, MD
Sydney M. & Stella H. Schoenberg Professor of Medicine
Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery and Cell Biology and Physiology
Chief, Division of Bone and Mineral Diseases
Musculoskeletal Research Center
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Declarações
RC is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research (position ending 31/12/2022).
Mahshid Mohseni, MD, MSci
Assistant Professor
Director, Clinical Research Unit
Co-Director, Clinical Operations
Division of Bone and Mineral Diseases
Department of Medicine
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Declarações
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Roberto Civitelli and Dr Mahshid Mohseni would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Julia F. Charles, Dr Camilo Restrepo, and Dr Javad Parvizi, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
JFC has received royalties from Up To Date, Waltham, MA, for authorship on articles relating to PDB; received grant funding from the National Institues of Health, the Rheumatology Research Foundation, and Brigham and Women's Hospital for research into regulation of osteoclast function, but not specifically relating to PDB; and had a manuscript published from a collaboration with Dr Jae Shim describing a pagetic phenotype in mice with osteoclast-specific loss of Chmp5. CR and JP are authors of a reference cited in this topic.
Revisores
Frederick Singer, MD
Director
Endocrine/Bone Disease Program
John Wayne Cancer Institute
Santa Monica
CA
Declarações
FS declares that he has no competing interests.
Joseph Lane, MD
Orthopaedic Surgeon
Hospital for Special Surgery
New York
NY
Declarações
JL declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Tuck SP, Walker J. Adult Paget's disease of bone. Clin Med (Lond). 2020 Nov;20(6):568-71.Texto completo Resumo
Singer FR, Bone HG 3rd, Hosking DJ, et al. Paget's disease of bone: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Dec;99(12):4408-22.Texto completo Resumo
Whitehouse RW. Paget's disease of bone. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2002 Dec;6(4):313-22. Resumo
Ralston SH, Corral-Gudino L, Cooper C, et al. Diagnosis and management of Paget's disease of bone in adults: a clinical guideline. J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Apr;34(4):579-604.Texto completo Resumo
Cooper C, Dennison E, Schafheutle K, et al. Epidemiology of Paget's disease of bone. Bone. 1999;24:3S-5S. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Osteomalácia
- Displasia fibrosa
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Diagnosis and management of Paget's disease of bone in adults
- Paget’s disease of bone
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal