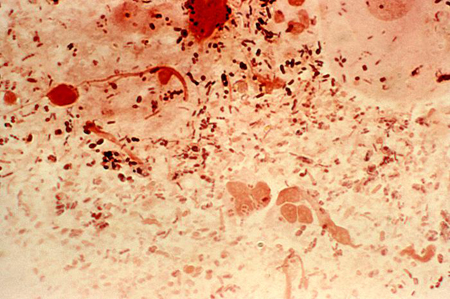
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presença de fatores de risco
- secreção uretral em homens
- sensibilidade e/ou inchaço do epidídimo
- exsudato mucopurulento ou purulento na endocérvix
Other diagnostic factors
- dor pélvica em mulheres
- irritação uretral em homens
- disúria em homens
- sensibilidade e/ou inchaço dos testículos
- sensibilidade e/ou inchaço da próstata
- prurido anal
- secreção mucopurulenta do reto
- dor no reto
- tenesmo
- sangramento retal
- corrimento vaginal
- friabilidade cervical
- sensibilidade uterina, anexial ou dor à mobilização do colo
- massa uterina
- linfadenopatia cervical anterior
- conjuntivite
- febre
- lesões cutâneas (pápulas, bolhas, petéquias ou necróticas) nos membros
- poliartrite
- erupção cutânea púrpura
- sinal de Brudzinski e sinal de Kernig positivo
- convulsões
- sinais cerebrais focais
- sopros
- oftalmia neonatal
- rinite
- uretrite (infantil)
- vaginite
Risk factors
- idade de 20 a 24 anos
- homens que fazem sexo com homens (HSH)
- ascendência negra
- histórico atual ou anterior de IST
- vários parceiros sexuais recentes
- uso inconsistente de preservativo
- fatores de risco do parceiro
- história de abuso sexual ou físico
- uso de substâncias
- passagem pela prisão
- comunidade com alta morbidade
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- teste de amplificação de ácido nucleico (NAAT)
- cultura
- urinálise em homens
- coloração de Gram no sedimento urinário
- coloração de Gram da secreção uretral
- teste de HIV
- Teste de sífilis
Tests to consider
- ultrassonografia transvaginal
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) ou ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) pélvica
Treatment algorithm
não gestante >45 kg: infecção urogenital/anorretal não complicada ou infecção faríngea (excluindo a infecção geniturinária complicada)
não gestante >45 kg: infecção geniturinária complicada
não gestante >45 kg: infecção gonocócica disseminada
gestante: infecção urogenital/anorretal não complicada ou infecção faríngea (excluindo a infecção geniturinária complicada)
gestante: infecção complicada
neonato
criança ≤45 kg
recorrente/resistente: infecção urogenital/anorretal ou faringite
Contributors
Authors
Sheldon Morris, MD, MPH
Assistant Professor
Division of Infectious Diseases
Department of Medicine
UCSD Antiviral Research Center
Division of Family Medicine
Department of Family and Preventive Medicine
UCSD La Jolla Family and Sports Medicine
San Diego
CA
Disclosures
SM has received research funding via his institution from Merck, Gilead Sciences, National Institutes of Health, California HIV/AIDS Research Program, and California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. He has completed a National Institutes of Health contract for research study on the Visby Medical Sexual Health Test. He holds stock in Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer. He is a co-founder of Aspera Biomedicines and a consultant for Primmune Therapeutics. SM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Vani Dandolu, MD, MPH
Associate Professor
Ob/Gyn and Urology
Director
Division of Urogynecology
Associate Residency Program Director
Temple University Hospital
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
VD declares that he has no competing interests.
Eva Jungmann, FRCP MSc
Consultant in Genitourinary and HIV Medicine
Archway Centre & Mortimer Market Centre
London
UK
Disclosures
EJ declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. 2016 [internet publication].Full text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonococcal isolate surveillance project (GISP). 30 August 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Jul 23;70(4):1-187.Full text Abstract
Miller WC, Ford CA, Morris M, et al. Prevalence of chlamydial and gonococcal infections among young adults in the United States. JAMA. 2004 May 12;291(18):2229-36.Full text Abstract
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae - 2014. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2014 Mar 14;63(RR-02):1-19.Full text Abstract
Fifer H, Saunders J, Soni S, et al. 2018 UK national guideline for the management of infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Int J STD AIDS. 2020 Jan;31(1):4-15.Full text Abstract
US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021 Sep 14;326(10):949-56.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
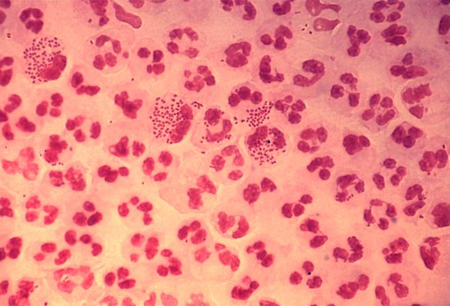
Differentials
- Infecção por clamídia
- Trichomonas
- Outras causas infecciosas de uretrite, cervicite, doença inflamatória pélvica (DIP) e epididimite
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Reducing sexually transmitted infections
- Guidance on the use of expedited partner therapy in the treatment of gonorrhea
More GuidelinesPatient information
Gonorreia
More Patient informationVideos
Demonstração animada de injeção intramuscular
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer