Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- história familiar de DRP autossômica dominante (DRPAD) ou doença renal em estágio terminal
- história familiar de evento cerebrovascular.
- cistos renais
- hipertensão
- dor abdominal/nos flancos
- hematúria
- massa abdominal/renal palpável
- cefaleias
- disúria, dor suprapúbica, febre
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- sopro cardíaco
- hérnia abdominal
- hepatomegalia
- dor torácica
Factores de riesgo
- história familiar de DRP autossômica dominante (DRPAD)
- história familiar de evento cerebrovascular.
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- ultrassonografia renal
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) de abdome/pelve
- RNM de abdome/pelve
- urinálise/cultura de urina e coloração de Gram
- eletrólitos séricos, ureia e creatinina
- perfil lipídico em jejum
- eletrocardiograma (ECG)
- TC cranioencefálica
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- teste genético
- ecocardiograma
- urina de 24 horas
- TC de dupla energia do abdome/pelve
- punção lombar e análise do líquido cefalorraquidiano
- proteína C-reativa
- tomografia por emissão de pósitrons (PET)
Algoritmo de tratamiento
doença policística autossômica dominante confirmada
doença renal em estágio terminal
Colaboradores
Autores
Marie C. Hogan, MD, PhD
Consultant
Division of Nephrology
Professor of Medicine
College of Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Divulgaciones
MCH receives research funding from Novartis, and was an investigator participating in tolvaptan clinical trials. MCH is also an author of several references cited in this topic.
Maria Irazabel Mira, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine, Associate Consultant
Division of Nephrology and Hypertension
Department of Internal Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Divulgaciones
MIM is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Agradecimientos
Dr Marie C Hogan and Dr Maria Irazabal Mira would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Vicente Torres, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures: VT is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Revisores por pares
Richard Sandford, PhD, FRCP
Wellcome Trust Senior Fellow in Clinical Research
University Reader in Real Genetics
Honorary Consultant in Medical Genetics
Cambridge
UK
Divulgaciones
RS declares that he has no competing interests.
Arlene Chapman, MD
Professor of Medicine
Renal Division
Emory University
School of Medicine
Atlanta
GA
Divulgaciones
Not disclosed.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Bergmann C, Guay-Woodford LM, Harris PC, et al. Polycystic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018 Dec 6;4(1):50.Texto completo Resumen
Cornec-Le Gall E, Alam A, Perrone RD. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2019 Mar 2;393(10174):919-35. Resumen
Pei Y, Obaji J, Dupuis A, et al. Unified criteria for ultrasonographic diagnosis of ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Jan;20(1):205-12.Texto completo Resumen
Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, et al; TEMPO 3:4 Trial Investigators. Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367(25):2407-18.Texto completo Resumen
Schrier RW, Abebe KZ, Perrone RD, et al; HALT-PKD Trial Investigators. Blood pressure in early autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 11;371(24):2255-66. Resumen
Torres VE, Abebe KZ, Chapman AB, et al; HALT-PKD Trial Investigators. Angiotensin blockade in late autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 11;371(24):2267-76. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
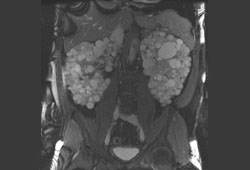
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Doença renal cística adquirida
- Cisto simples
- Complexo da esclerose tuberosa
Más Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): executive summary
- KHA-CARI autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease guidelines
Más DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Nefrolitíase
Infecção renal
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesCalculadoras
Taxa de filtração glomerular estimada pela equação de estudo em MDRD rastreável por IDMS
Mais CalculadorasVideos
Punção lombar diagnóstica em adultos: demonstração animada
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal