შეჯამება
განსაზღვრება
ანამნეზი და გასინჯვა
ძირითადი დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- presença de fatores de risco
- formação de bolhas erosivas crônica da pele, mucosa ou ambas
- erosões crônicas da boca (pênfigo vulgar [PV], pênfigo paraneoplásico [PPN])
- lábios dolorosos (PPN)
- dispneia (PPN)
სხვა დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- couro cabeludo pruriginoso (PV, PF)
- epistaxe (PV, PPN)
- pele dolorosa (PV, PF, PPN)
- disfagia (PV)
- pele pruriginosa (PV, PF)
- conjuntivite (PV, PPN)
რისკფაქტორები
- idade mais avançada
- HLA DR4 (pênfigo vulgar [PV])
- HLA DQ1 (PV)
- HLA DRB1 (pênfigo paraneoplásico [PPN])
- neoplasia maligna subjacente (PPN)
- uso de penicilamina
- uso de IECAs
- uso de penicilina
- uso de tiopronina
- uso de interleucina-2
- uso de nifedipino
- uso de rifampicina
- exposição a insetos hematófagos
დიაგნოსტიკური კვლევები
1-ად შესაკვეთი გამოკვლევები
- biópsia de pele, coloração de hematoxilina e eosina
- biópsia de pele, imunofluorescência direta
გასათვალისწინებელი კვლევები
- imunofluorescência indireta em soro
- ensaio de imunoadsorção enzimática (ELISA) sérico
- endoscopia digestiva alta
- radiografia torácica
- tomografia do tórax
- testes de função pulmonar (TFPs)
- imunoblot sérico (Western Blot)
მკურნალობის ალგორითმი
pênfigo vulgar leve
pênfigo foliáceo leve
pênfigo vulgar ou pênfigo foliáceo moderado a grave
pênfigo paraneoplásico
pênfigo vulgar ou pênfigo foliáceo moderado a grave 6 meses após a terapia inicial: com controle da doença/remissão completa
pênfigo vulgar ou pênfigo foliáceo moderado a grave 6 meses após a terapia inicial: com remissão completa
pênfigo vulgar ou pênfigo foliáceo moderado a grave 12 a 18 meses após a terapia inicial: remissão completa
pênfigo grave/refratário
კონტრიბუტორები
ავტორები
Jon H. Meyerle, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Dermatology
Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
Bethesda
MD
გაფრთხილება:
JHM declares that he has no competing interests.
Grant J. Anhalt, MD
Professor
Department of Dermatology
Johns Hopkins Medical Institution
Baltimore
MD
გაფრთხილება:
GJA declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტები
Daniel Mimouni, MD
Professor
Department of Dermatology
Rabin Medical Center
Petah Tikva
Israel
Disclosures
DM declares that he has no competing interests.
Vesna Petronic-Rosic, MD, MSc
Associate Professor and Clinical Director
Section of Dermatology
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
VPR declares that she has no competing interests.
Timothy Patton, MD
Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Department of Dermatology
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
Disclosures
TP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Joly P, Horvath B, Patsatsi Α, et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Sep;34(9):1900-13.Full text Abstract
Antiga E, Bech R, Maglie R, et al. S2k guidelines on the management of paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 Jun;37(6):1118-34.Full text Abstract
Murrell DF, Peña S, Joly P, et al. Diagnosis and management of pemphigus: recommendations of an international panel of experts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar;82(3):575-85.e1.Full text Abstract
Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux 3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2017 May 20;389(10083):2031-40. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
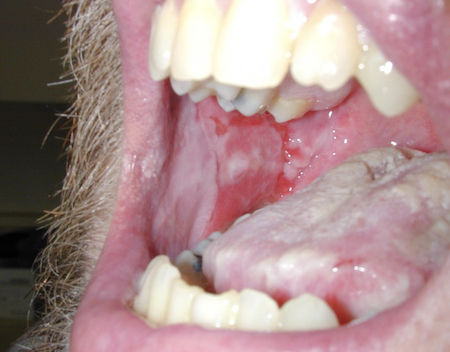
Differentials
- Pênfigo benigno familiar (doença de Hailey-Hailey)
- Penfigoide bolhoso (PB)
- Dermatose linear bolhosa por imunoglobulina A (IgA)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Consensus based Indian guidelines for the management of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceous
- S2k guidelines on the management of paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV)
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer