Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- dor de ouvido
- sensibilidade sobre ao longo do trago, da pina ou de ambos
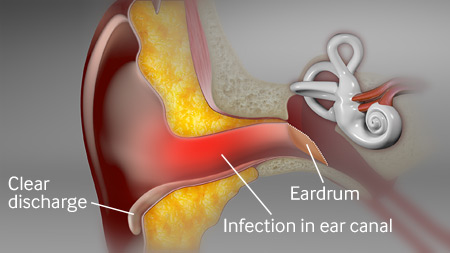
- edema e eritema do meato acústico externo
- tecido de granulação no meato acústico externo (otite externa necrotizante)
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- otorreia
- plenitude aural
- prurido
- perda auditiva
- dor intensificada pelo movimento da mandíbula
- membrana timpânica eritematosa
- celulite da pina e da pele adjacente
Fatores de risco
- obstrução do meato acústico externo
- umidade ambiental elevada
- temperaturas ambientais mais elevadas
- natação
- trauma local
- agentes químicos irritantes
- alergia
- afecção cutânea
- diabetes
- imunocomprometido
- uso prolongado de agentes antibacterianos tópicos
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- otoscopia pneumática
- timpanometria
Investigações a serem consideradas
- cultura da orelha
- microscopia de exsudato/detritos do meato acústico externo
- TC do osso temporal com contraste intravenoso
- RNM do cérebro e dos meatos acústicos internos (com e sem gadolínio)
- velocidade de hemossedimentação (VHS)
Algoritmo de tratamento
bacteriana
fúngica
Colaboradores
Autores
Soha Ghossaini, MD, FACS
Otology-Neurotology
ENT and Allergy Associates LLP
Flushing
New York
NY
Declarações
SG declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
We would like to acknowledge our ENT expert panel member, Dr Lawrence Lustig, for his contribution to this topic. Dr Lustig declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Peter S. Roland, MD
Professor Neurological Surgery
Chief of Pediatric Otology
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Dallas
TX
Declarações
PSR has acted as a consultant to Alcon Laboratories, maker of Ciprodex®, which has provided compensation to the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. PSR has received compensation for speaking and for organising educational events. PSR is co-author of the American Academy of Head and Neck Surgery's practice guideline for acute otitis externa. PSR is an author of references cited in this topic.
Anthony Wright, LLM, DM, FRCS
Emeritus Professor of Otolaryngology
UCL Ear Institute
London
UK
Declarações
AW declares that he has no competing interests.
Desmond A. Nunez, MD, FRCS(ORL)
Director ENT Unit
North Bristol NHS Trust
Honorary Reader in Otolaryngology
University of Bristol
Bristol
UK
Declarações
DAN declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Cannon CR, et al. American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation. Clinical practice guideline: acute otitis externa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Feb;150(1 suppl):S1-24. [Erratum in: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Mar;150(3):504].Texto completo Resumo
Jackson EA, Geer K. Acute otitis externa: rapid evidence review. Am Fam Physician. 2023 Feb;107(2):145-51. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Otite média aguda
- Furunculose
- Dermatite de contato do meato acústico externo
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- ACR appropriateness criteria: inflammatory ear disease
- Clinical practice guideline: acute otitis externa
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Infecção da orelha externa
Infecções otológicas em crianças: perguntas a fazer ao seu médico
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesVideos
Como examinar a orelha
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal