Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- dor inespecífica no local da infecção
- dorsalgia
- mal-estar e fadiga
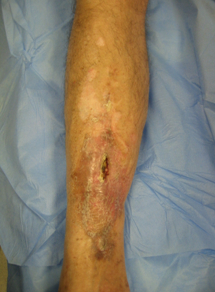
- inflamação local, eritema ou edema
- febre baixa
- presença de fatores de risco
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- drenagem da ferida e/ou do trato sinusal
- amplitude de movimento reduzida
- sensação reduzida
- sintomas do trato urinário
- torcicolo
- deformidade dos membros
- sensibilidade à percussão
Fatores de risco
- osteomielite prévia
- lesões penetrantes
- contaminação cirúrgica
- infecções distantes ou locais
- uso indevido de substâncias por via intravenosa
- diabetes mellitus
- periodontite
- imunocomprometimento
- anemia falciforme
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- contagem leucocitária
- velocidade de hemossedimentação
- proteína C-reativa
- radiografia simples da área afetada
- hemocultura
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) do osso
- biópsia dos ossos guiada ou biópsia dos ossos aberta
Investigações a serem consideradas
- ultrassonografia
- Tomografia computadorizada (TC)
- cintilografia com radionuclídeos
- cintilografia óssea trifásica
- histologia
Algoritmo de tratamento
suspeita de osteomielite periférica aguda: baixa prevalência de MRSA
suspeita de osteomielite periférica aguda: alta prevalência de MRSA
suspeita de osteomielite vertebral nativa aguda
suspeita de osteomielite aguda em pé diabético
osteomielite periférica aguda confirmada: adultos e crianças
osteomielite vertebral nativa aguda confirmada: adultos e crianças
osteomielite aguda confirmada no pé diabético: adultos e crianças
osteomielite crônica
Colaboradores
Autores
Tessa Gomez, MD
Attending, Department of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases, Mount Sinai Beth Israel
Associate Professor, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York
NY
Declarações
TG declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Tessa Gomez would like to gratefully acknowledge Mr Adrian Kendal, Dr Jamie Ferguson, Dr Tse Hua Nicholas Wong, Dr Bridget L. Atkins, Dr Martin McNally, Dr Jason H. Calhoun, Dr Nalini Rao, and Dr M.M. Manring, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
JF received a research grant in 2013 from Bonesupport AB, Lund, Sweden to collect data for a study on antibiotic carriers in osteomyelitis treatment. JF is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. BLA is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. MM is an executive board member of the European Bone & Joint Infection Society and the Girdlestone Orthopaedic Society. He has performed consultancy work for Bonesupport AB and the Oxford Bone Infection Consultancy. He has received travel expenses from Bonesupport AB and the AO Foundation to attend scientific conferences and symposia. He has received royalties from Oxford University Press for contributions to textbooks. MM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. AK, THNW, JHC, NR, and MMM declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Kristine Johnson, MD
Assistant Professor
Infectious Diseases
Bayview Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
KJ declares that she has no competing interests.
Silvano Esposito, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Infectious Diseases
University of Naples
Naples
Italy
Disclosures
SE has been reimbursed for attending several conferences and received fees for speaking and running educational programs by Pfizer, Novartis, Wyeth Lederle, Sanofi Aventis, and GSK.
Edward Pesanti, MD
Professor of Medicine
Infectious Diseases Division
University of Connecticut Health Center
Hartford
CT
Disclosures
EP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Woods CR, Bradley JS, Chatterjee A, et al. Clinical practice guideline by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2021 guideline on diagnosis and management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in pediatrics. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021 Sep 23;10(8):801-44.Full text Abstract
Berbari EF, Kanj SS, Kowalski TJ, et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 15;61(6):e26-46.Full text Abstract
Lipsky BA, Senneville É, Abbas ZG, et al; International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF). Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of foot infection in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Mar;36 Suppl 1:e3280.Full text Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, or soft tissue infection (excluding spine and diabetic foot). 2022 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Artrite séptica
- Artrite idiopática juvenil
- Sinovite transitória
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis of the foot in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Guide to utilization of the microbiology laboratory for diagnosis of infectious diseases: 2024 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society for Microbiology (ASM)
More GuidelinesPatient information
Osteomielite
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer