Resumo
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presença de fatores de risco
- erupção cutânea polimorfa
- hiperemia conjuntival
- mucosite
- alterações cutâneas nos membros periféricos
- linfonodos cervicais aumentados
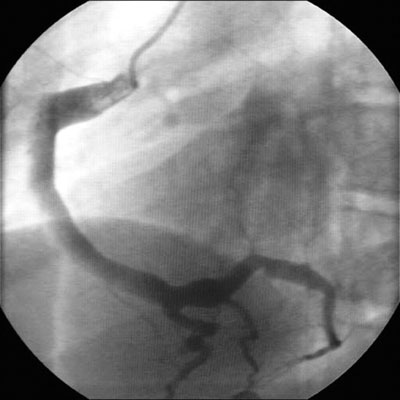
- aneurismas da artéria coronária
- febre e irritabilidade extrema
Other diagnostic factors
- pericardite com efusão
- insuficiência cardíaca congestiva
- dor na articulação ou edema
- rouquidão
- manifestações neurológicas
- manifestações gastrointestinais
- manifestações urológicas
- outras manifestações dermatológicas
Risk factors
- ascendência asiática
- 3 meses a 4 anos de idade
- sexo masculino
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- Hemograma completo
- velocidade de hemossedimentação (VHS)
- proteína C-reativa sérica
- ecocardiograma
- testes séricos da função hepática
- urinálise
- eletrocardiograma
Tests to consider
- radiografia torácica
- ultrassonografia da vesícula biliar
- ultrassonografia dos testículos
- punção lombar
- angiografia por tomografia computadorizada
- angiografia por ressonância magnética (ARM)
- cateterismo cardíaco e angiografia
Emerging tests
- testes de peptídeos natriuréticos
Treatment algorithm
apresentação ≤10 dias a partir do início; ou apresentação >10 dias do início com evidências de inflamação contínua
apresentação >10 dias do início sem evidências de inflamação contínua
após o episódio inicial: Z-score sempre <2; sem comprometimento em nenhum momento
após o episódio inicial: Z-score ≥2.0 a <2.5; apenas dilatação
após episódio inicial: Z-score ≥2.5 a <5.0; aneurisma pequeno
após o episódio inicial: Z-score ≥5 a <10 (com dimensão luminal absoluta <8 mm); aneurisma médio
após episódio inicial: Z-score ≥10 ou diâmetro luminal absoluto ≥8 mm; aneurisma grande ou gigante
Contributors
Authors
Paul Brogan, BSc(Hon), MBChB(Hon), FRCPCH, MSc, PhD
Professor of vasculitis
University College London
London
UK
Disclosures
PB is chief investigator of the KDCAAP trial, results pending; trustee of Societi, a patient KD organisation; and is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Kirsty McLellan, BMedSci, MBChB, MRCPCH
Specialist Registrar in Paediatric Rheumatology
Great Ormond Street Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
KM declares she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Paul Brogan and Dr Kirsty McLellan would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Abraham Gedalia and Dr James Krulisky, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
AG declares that he has no competing interests. JK declares that he is a paid consultant for Axia Medical Solutions, a small skincare company from Carlsbad, CA.
Peer reviewers
Michael Levin, null
Professor of International Child Health
Imperial College London
London
Disclosures
ML declares that he has no competing interests.
Kirsten Bourke Dummer, MD
Clinical Professor, Pediatrics
Division of Pediatric Cardiology
UC San Diego/Rady Children’s Hospital
San Diego
CA
Disclosures
KBD declares that she has no competing interests.
David Burgner, BSc(Hons), MBChB, MRCP, MRCPCH, FRACP, DTMH, PhD
Principal Research Fellow
Murdoch Childrens Research Institute
The Royal Children’s Hospital
Victoria
Australia
Disclosures
DB has received competitive research funding from the National Heart Foundation Australia and from the Agency for Science, Technology and Research of the Singapore Government. He is co-inventor on a patent related to diagnostics submitted through the Genome Institute of Singapore.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, et al; American Heart Association. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-99.Full text Abstract
de Graeff N, Groot N, Ozen S, et al. European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Apr 1;58(4):672-82.Full text Abstract
Jone PN, Tremoulet A, Choueiter N, et al. Update on diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024 Dec 3;150(23):e481-500.Full text Abstract
Gorelik M, Chung SA, Ardalan K, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation guideline for the management of Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022 Apr;74(4):538-48. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Infecção por estafilococos ou estreptococos
- Artrite idiopática juvenil sistêmica
- Escarlatina
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Update on diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association
- European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer