Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- dor abdominal
- amenorreia
- sangramento vaginal
- desconforto abdominal
- sensibilidade ou massa anexial
- sangue na cúpula vaginal
- instabilidade hemodinâmica, hipotensão ortostática
- dor à mobilização do colo
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- desejo de defecar
- dor referida no ombro
Fatores de risco
- gravidez ectópica prévia
- cirurgia de esterilização tubária prévia
- exposição ao dietilestilbestrol no útero da mãe
- uso de dispositivo intrauterino (DIU)
- infecções genitais prévias
- salpingite crônica
- salpingite ístmica nodosa
- infertilidade
- múltiplos parceiros sexuais
- tabagismo
- raça/etnia
- tecnologia de reprodução assistida
- primeiro contato sexual <18 anos
- idade materna >35 anos
- cirurgia de reconstrução tubária
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- teste de gravidez urinário ou sérico
- ultrassonografia transvaginal (USTV) de alta resolução
- ultrassonografia transabdominal
Investigações a serem consideradas
- gonadotrofina coriônica humana (hCG) sérica serial
- aspiração uterina
Algoritmo de tratamento
gravidez ectópica tubária: gravidez ectópica rota ou fracasso do tratamento clínico
gravidez ectópica tubária: risco moderado ou fracasso na conduta expectante
gravidez ectópica tubária: baixo risco
Colaboradores
Autores
Kurt T. Barnhart, MD, MSCE
William Shippen Jr. Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Epidemiology
Vice Chair for Clinical Research
Director, Women's Health Clinic Research Center
The Perelman School of Medicine
University of Pennsylvania
Associate Chief, Penn Fertility Care
Philadelphia
PA
Declarações
KTB is a co-author on several papers cited in this topic.
Agradecimentos
Dr Kurt T. Barnhart would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ingrid Granne, Dr Veronica Gomez-Lobo, Dr Sina Haeri, and Dr Mohammad Ezzati, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
IG, VGL, SH, and ME declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Alan Decherney, MD
Chief
Reproductive Biology Medicine and Biology
NICHD
Bethesda
MD
Declarações
AD declares that he has no competing interests.
Joanna C. Girling, MA, MRCP, FRCOG
Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
West Middlesex University Hospital
London
UK
Declarações
JCG declares that she has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
ACOG practice bulletin no. 193: tubal ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Mar;131(3):e91-103. Resumo
Kirk E, Bottomley C, Bourne T. Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location. Hum Reprod Update. 2014 Mar-Apr;20(2):250-61.Texto completo Resumo
Elson CJ, Salim R, Potdar N, et al; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy: Green-top Guideline No. 21. BJOG. 2016 Dec;123(13):e15-55.Texto completo Resumo
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage: diagnosis and initial management. Nov 2021 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
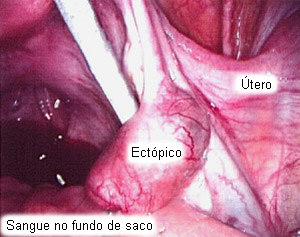
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Aborto espontâneo
- Apendicite aguda
- Torção ovariana
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage: diagnosis and initial management
- ACR appropriateness criteria: acute pelvic pain in the reproductive age group
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Gravidez ectópica: o que é?
Gravidez ectópica: quais são as opções de tratamento?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal