Summary
Definition
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- presença de fatores de risco
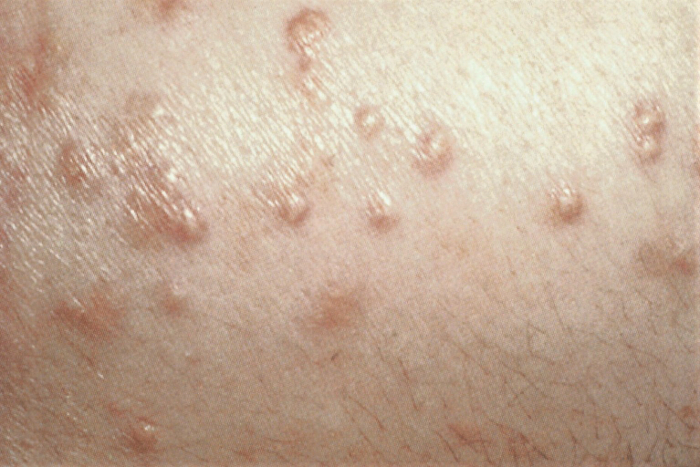
- xantomas eruptivos
- lipemia retiniana
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- IMC/circunferência da cintura elevada
- lipodistrofia
- características da doença arterial coronariana
- claudicação
- características neurológicas
- dor abdominal recorrente
Factores de riesgo
- história familiar de hiperlipidemia
- dieta rica em gordura saturada
- dieta rica em carboidratos ou alto índice glicêmico
- consumo excessivo de álcool
- história familiar ou pessoal de sobrepeso/obesidade
- história familiar ou pessoal de diabetes
- resistência insulínica
- doença hepática
- doença renal
- Infecção pelo vírus da imunodeficiência humana (HIV)
- uso de determinados medicamentos
- Síndrome de Cushing
- distúrbios inflamatórios/imunológicos
- transplante de órgãos
- hipotireoidismo
- gestação
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- nível de triglicerídeos
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- apolipoproteína B
- glicemia de jejum
- ureia, creatinina
- albumina/proteína urinária
- albumina sérica
- hormônio estimulante da tireoide
- testes da função hepática
- proteína C-reativa
Algoritmo de tratamiento
quilomicronemia
HTG moderada (triglicerídeos em jejum ≥1.7 mmol/L [≥150 mg/dL] ou triglicerídeos sem jejum ≥2.0 mmol/L [≥175 mg/dL] e triglicerídeos <5.6 mmol/L [<500 mg/dL])
HTG grave (triglicerídeos em jejum ≥5.6 mmol/L [≥500 mg/dL] especialmente triglicerídeos em jejum ≥11.3 mmol/L [≥1000 mg/dL])
Colaboradores
Autores
Robert A. Hegele, MD, FRCPC, Cert Endo, FACP, FAHA
Jacob J. Wolfe Distinguished Medical Research Chair
Martha Blackburn Chair in Cardiovascular Research
Distinguished University Professor of Medicine and Biochemistry
University of Western Ontario
London
Ontario
Canada
Divulgaciones
RAH reports consulting fees from Akcea/Ionis, Amgen, HLS Therapeutics, Medison, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi and Ultragenyx. RAH is an author of references cited in this topic.
Agradecimientos
Dr Robert A. Hegele would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr David Alexander Leaf, the previous contributor to this topic.
Divulgaciones
DAL declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Vinaya Simha, MBBS, MD
Associate Professor
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Divulgaciones
VS declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2019 Jun 18;139(25):e1082-143.Texto completo Resumen
Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020 Jan 1;41(1):111-88.Texto completo Resumen
Patel SB, Wyne KL, Afreen S, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology clinical practice guideline on pharmacologic management of adults with dyslipidemia. Endocr Pract. 2025 Feb;31(2):236-62.Texto completo Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Diabetes
- Lipodistrofias
- Doença hepática
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- AACE Consensus Statement: Algorithm for Management of Adults with Dyslipidemia – 2025 Update
- 2025 AACE clinical practice guidelines on the pharmacologic management of adults with dyslipidemia
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Colesterol alto
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad