Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- maior susceptibilidade a infecções
- distúrbios do paladar
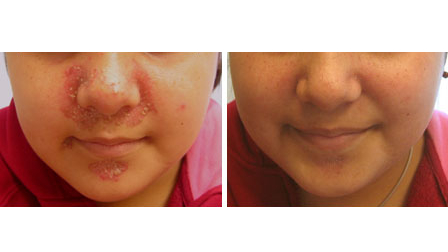
- estomatite
- cicatrização tardia de ferida
- acrodermatite enteropática
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- fadiga
- sintomas gastrointestinais
- baixa estatura
- fratura óssea
- intolerância à glicose
- dermatite
- perda de peso
- alopécia
- paroníquia
- febre
- tremor de intenção
- depressão
- comprometimento da concentração
- nistagmo
- disartria
- cegueira noturna
- hipogeusia
- anosmia
- blefarite
- demência
Fatores de risco
- viver em regiões em desenvolvimento
- idade >65 anos
- doença gastrointestinal e hepática crônica
- doença renal
- doença falciforme
- tratamento crônico com hidroclorotiazida, penicilamina, etambutol, determinados antibióticos
- Infecção pelo vírus da imunodeficiência humana (HIV)
- transtornos decorrentes do uso de bebidas alcoólicas
- dietas vegetariana/vegana em longo prazo
- dietas para perda de peso especializadas
- bebês com dietas pobres em nutrientes
- história familiar de deficiência de zinco
- anorexia nervosa
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- níveis de zinco sérico ou plasmático
- nível de ferro sérico
- nível de 25-OH vitamina D
- folato sérico
- vitamina B12 sérica
Novos exames
- conteúdo de zinco celular
- teste genético para acrodermatite enteropática
Algoritmo de tratamento
adquirida
acrodermatite enteropática
Colaboradores
Autores
Prashant Singh, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
USA
Declarações
PS declares that he has no competing interests.
Judy Nee, MD
Instructor in Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Boston
MA
Declarações
JN declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Prashant Singh and Dr Judy Nee would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Daniel Leffler, a previous contributor to this topic.
Declarações
DL declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Hajo Haase, PhD
Assistant Professor for low molecular weight immune regulators
Institute of Immunology
University Hospital
RWTH Aachen University
Aachen
Germany
Declarações
HH has been reimbursed by Kohler Pharma, the manufacturer of UNIZINK, for attending a symposium and has received a fee for speaking at that symposium. HH is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Andrew Fenves, MD
Professor of Medicine
Baylor University Medical Center
Dallas
TX
Declarações
AF declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Immigrant and refugee health: nutrition and growth. May 2025 [internet publication].Texto completo
Lassi ZS, Kurji J, Oliveira CS, et al. Zinc supplementation for the promotion of growth and prevention of infections in infants less than six months of age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 8;4:CD010205.Texto completo Resumo
U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. Dec 2020 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Hipotireoidismo
- Depression
- Deficiência de ferro
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Nutrition and growth refugee healthy domestic guidance
- 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Mais DiretrizesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal