Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
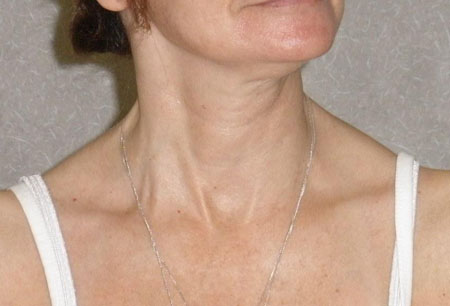
- torção ou desvio involuntário do pescoço
- dor cervical
- presença de truque sensorial
- postura anormal da cabeça
- restante do exame neurológico normal
Other diagnostic factors
- tremor da cabeça
- início insidioso
- cefaleia
- hipertrofia assimétrica dos músculos do pescoço
- amplitude de movimentos (ADM) normal do pescoço (no início da evolução)
Risk factors
- sexo feminino
- meia idade (40 a 59 anos)
- ascendência branca
- história familiar de torcicolo adquirido
- exposição a medicamentos bloqueadores da dopamina
- história de trauma
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- diagnóstico clínico
Tests to consider
- radiografias cervicais
- TC ou RNM cranioencefálica
- TC ou RNM do pescoço
- gene DYT-1
- ceruloplasmina sérica, excreção urinária de cobre
- eletromiografia
Treatment algorithm
indolor ou sem comprometimento funcional
com comprometimento funcional, dor ou diminuição da qualidade de vida
refratário à terapia com toxina botulínica
Contributors
Authors
David B. Sommer, MD, MPH

Neurologist and Movement Disorder Specialist
Reliant Medical Group
Worcester
MA
Disclosures
DBS declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr David B. Sommer would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Mark A. Stacy, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
MAS has received speaking honoraria and consulting fees from Allergan, the manufacturer of Botox; he has received research grant support from Ipsen, manufacturer of Dysport, and Merz, manufacturer of Xeomin; he is an author of a reference cited in this topic. Duke University has received funding from Allergan for a continuing medical education programme.
Peer reviewers
Allison Brashear, MD
Professor and Chair
Department of Neurology
Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center
Winston Salem
NC
Divulgaciones
AB declares interests in Allergan; she is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Robert Werner, MD
Professor
Chief of PM&R
Ann Arbor VA Medical Center
Ann Arbor
MI
Divulgaciones
RW declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Stacy M. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis of cervical dystonia. Neurol Clin. 2008 May;26(suppl 1):23-42. Resumen
Singer C, Velickovic M. Cervical dystonia: etiology and pathophysiology. Neurol Clin. 2008 May;26(suppl 1):9-22. Resumen
Colosimo C, Suppa A, Fabbrini G, et al. Craniocervical dystonia: clinical and pathophysiological features. Eur J Neurol. 2010 Jul;17(suppl 1):15-21. Resumen
Rodrigues FB, Duarte GS, Marques RE, et al. Botulinum toxin type A therapy for cervical dystonia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 12;11:CD003633.Texto completo Resumen
Dashtipour K, Lew M. Cervical dystonia. In: Stacy MA, ed. Handbook of dystonia. New York, NY: Informa Healthcare; 2007:137-53.
Jankovic J, Leder S, Warner D, et al. Cervical dystonia: clinical findings and associated movement disorders. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):1088-91. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Artrite da coluna cervical
- Massa cervical
- Massa, lesão ou infarto cerebral
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- Practice guideline update summary: botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache
- EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of primary dystonias
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Depressão em adultos: quais são as opções de tratamento?
Depressão em adultos: o que é?
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad