Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- perda de campo visual
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- cefaleia
- obscurecimentos visuais transitórios
- zumbido síncrono ao pulso
- fotofobia
- dor retrobulbar
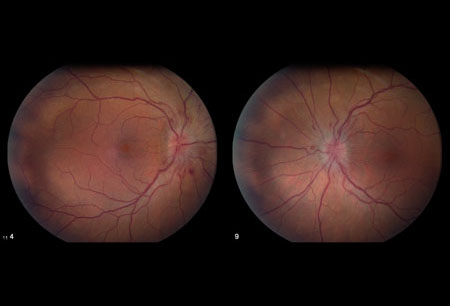
- edema do disco óptico
- acuidade visual reduzida
- distúrbios de motilidade ocular
- defeito pupilar aferente relativo
Fatores de risco
- sexo feminino
- obesidade e ganho de peso
- uso de determinados medicamentos
- doenças causais associadas
- apneia do sono
- história familiar
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- testes de campo visual (perimetria)
- fundoscopia dilatada
- acuidade visual
- ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) cranioencefálica com ou sem contraste
- punção lombar nos segmentos L3/L4 da espinha
Investigações a serem consideradas
- venografia por ressonância magnética da cabeça
- tomografia de coerência óptica
Algoritmo de tratamento
todos os pacientes
Colaboradores
Autores
Michael Wall, MD
Professor
Department of Neurology and Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences
University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics and Iowa City VA Health Care System
Iowa City
IA
Declarações
MW is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Mansoor Mughal, MD
Retina Fellow
Rutgers University
Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital
New Brunswick
NJ
Declarações
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Paul W. Brazis, MD
Consultant in Neurology and Neuro-Ophthalmology
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Declarações
PWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Tim D. Matthews, MBBS
Consultant Neuro-ophthalmologist
Birmingham Neuro-ophthalmology Unit
University Hospital Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Declarações
TDM declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Wall M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin. 2010 Aug;28(3):593-617.Texto completo Resumo
Johnson LN, Krohel GB, Madsen RW, et al. The role of weight loss and acetazolamide in the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Ophthalmology. 1998 Dec;105(12):2313-7. Resumo
Hayreh SS. Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc (papilloedema): a preliminary report. Br J Ophthalmol. 1964 Oct;48:522-43.Texto completo Resumo
Smith JL. Whence pseudotumor cerebri? J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1985 Mar;5(1):55-6. Resumo
Frisen L. Swelling of the optic nerve head: a staging scheme. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Jan;45(1):13-8.Texto completo Resumo
NORDIC Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Study Group Writing Committee; Wall M, McDermott MP, Kieburtz KD, et al. Effect of acetazolamide on visual function in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension and mild visual loss: the idiopathic intracranial hypertension treatment trial. JAMA. 2014 Apr 23-30;311(16):1641-51.Texto completo Resumo
Sinclair AJ, Burdon MA, Nightingale PG, et al. Low energy diet and intracranial pressure in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2010 Jul 7;341:c2701.Texto completo Resumo
Hoffmann J, Mollan SP, Paemeleire K, et al. European Headache Federation guideline on idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Headache Pain. 2018 Oct 8;19(1):93.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Anomalias estruturais intracranianas
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- European Headache Federation guideline on idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Zumbido
Obesidade - medicamentos e cirurgia
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal