Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- febre
- dor e disfagia
- edema facial
- edemas doloridos recorrentes
- exsudatos de pus pela abertura da glândula salivar
- uso de medicamentos xerostômicos
- trismos mandibulares
- dificuldade respiratória (estridor, uso de músculos acessórios, batimento da asa do nariz, sibilo)
- paralisia do nervo craniano
- doença do tecido conjuntivo ou síndrome de Sjögren
Other diagnostic factors
- edema episódico durante a alimentação
- recentes intervenções cirúrgicas sob anestesia geral
- ressecamento dos olhos e da boca
- candidíase oral
- exposição ao contraste iodado
- edemas indolores recorrentes
- deslocamento do lobo auricular
- pródromo de parestesia na glândula afetada
- edema no palato duro
Risk factors
- depleção de volume e desnutrição
- imunossupressão
- Síndrome de Sjögren
- doenças do tecido conjuntivo
- mulheres entre 50 e 60 anos de idade
- anestesia geral
- medicamentos xerostômicos
- sialolitíase
- obstrução mecânica crônica e/ou múltiplos episódios de inflamação aguda
- trauma (morder a bochecha)
- procedimentos ortodônticos/dentários
- sialectase, diverticulite e estenoses
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- cultura e sensibilidades do exsudato do ducto
- Hemograma completo
- radiografias faciais (filmes oclusais e/ou dos tecidos moles)
Investigations to consider
- ultrassonografia da glândula afetada
- Tomografia computadorizada (TC)
- sialografia digital por subtração
- Sialografia por ressonância magnética (RM)
- cintilografia usando radioisótopo pertecnetato Tc 99m de sódio
- anticorpos anti-SSA/Ro, anti-SSB/La
- fator antinuclear
- fator reumatoide
- citologia por aspiração com agulha fina (FNAC) da glândula afetada
- RNM
- biópsia das glândulas salivares menores
- IgG4 e IgE
- biópsia das glândulas salivares maiores
- sialoendoscopia
Treatment algorithm
sinais de comprometimento das vias aéreas
sialadenite bacteriana aguda (não obstrutiva)
sialadenite obstrutiva
sialadenite autoimune
sialadenite necrosante subaguda
sialadenite crônica: recorrente ou esclerosante (<3 vezes/ano ou não grave)
sialadenite recorrente: qualquer causa (>3 vezes/ano ou ataques graves)
Contributors
Authors
Chris Avery, MD, MChir, FDSRCS, FRCS, FRCS (OMFS)
Consultant Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
Honorary Associate Professor Senior Lecturer
University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust
Leicester
UK
Disclosures
CA declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Chris Avery would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Alfredo Aguirre, Dr Michael N. Hatton, and Dr Ernesto de Nardin, previous contributors to this topic. AA, MNH, and EDN declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Issac van der Waal, DDS, PhD
Professor of Oral Pathology
Head of the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral Pathology
VU University Medical Centre and Academic Centre for Dentistry
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Declarações
IVDW declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael D. Turner, DDS, MD, FACS
Assistant Professor
New York University College of Dentistry
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of Periodontics and Implant Dentistry
New York University School of Medicine
New York
NY
Declarações
MDT declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Fattahi TT, Lyu PE, Van Sickels JE. Management of acute suppurative parotitis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:446-448. Resumo
Kraaij S, Karagozoglu KH, Forouzanfar T, et al. Salivary stones: symptoms, aetiology, biochemical composition and treatment. Br Dent J. 2014 Dec 5;217(11):E23.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
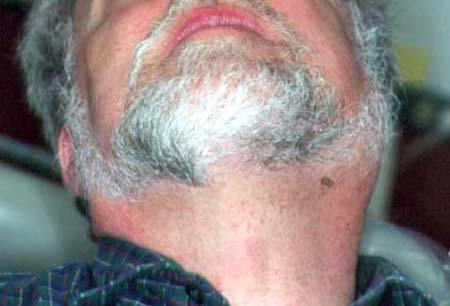
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Caxumba
- Sarcoidose
- Tuberculose
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Updated S2K AWMF guideline for the diagnosis and follow-up of obstructive sialadenitis - relevance for radiologic imaging
- Salivary gland disorders
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Artrite reumatoide
Sarampo, caxumba e rubéola: meu filho deve tomar a vacina tríplice viral?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal