Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- presença de fatores de risco
- visualização do cerume
- perda auditiva
- plenitude aural
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- otorreia
- otalgia
- zumbido
- tosse
- vertigem
Fatores de risco
- idade >50 anos ou <5 anos
- sexo masculino
- meato acústico externo estenótico
- Síndrome de Down
- uso de cotonetes
- uso de prótese auditiva
- morar em uma instituição asilar
Investigações diagnósticas
Investigações a serem consideradas
- audiograma
Algoritmo de tratamento
todos os pacientes
Colaboradores
Autores
Stephen Wetmore, MD, MBA, FACS

Professor Emeritus
Department of Otolaryngology
West Virginia University School of Medicine
Morgantown
WV
Declarações
SW declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores
Rahul K. Shah, MD, FAAP
Associate Professor of Otolaryngology and Pediatrics
Division of Otolaryngology
Children's National Medical Center
Assistant Professor
Otolaryngology and Pediatrics
George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Washington
DC
Declarações
RKS declares that he has no competing interests.
Seth R. Schwartz, MD, MPH
Director of Research
The Listen For Life Center At Virginia Mason
Otology/Otolaryngology
Department of Otolaryngology
Virginia Mason Medical Center
Seattle
WA
Declarações
SRS is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Robin Youngs, MD, FRCS
Consultant Otologist
Gloucestershire Royal Hospital
Gloucester
UK
Declarações
RY declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Schwartz SR, Magit AE, Rosenfeld RM, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): earwax (cerumen impaction). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;156(1_suppl):S1-29.Texto completo Resumo
Roeser RJ, Ballachanda BB. Physiology, pathophysiology, and anthropology/epidemiology of human ear canal secretions. J Am Acad Audiol. 1997;8:391-400. Resumo
Horton GA, Simpson MTW, Beyea MM, et al. Cerumen management: an updated clinical review and evidence-based approach for primary care physicians. J Prim Care Community Health. 2020 Jan-Dec;11:2150132720904181.Texto completo Resumo
Roland PS, Eaton DA, Gross RD, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled evaluation of Cerumenex and murine earwax removal products. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004 Oct;130(10):1175-7.Texto completo Resumo
Aaron K, Cooper TE, Warner L, et al. Ear drops for the removal of ear wax. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 25;7:CD012171.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
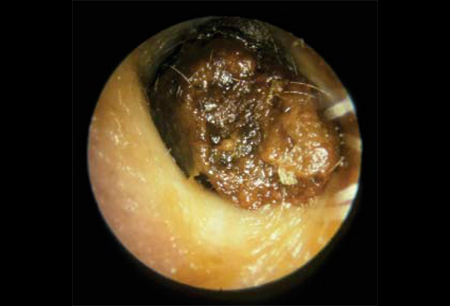
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Otite externa
- Ceratose obliterante
- Pólipo do meato acústico externo
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Clinical practice guideline (update): earwax (cerumen impaction)
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Cerume
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal