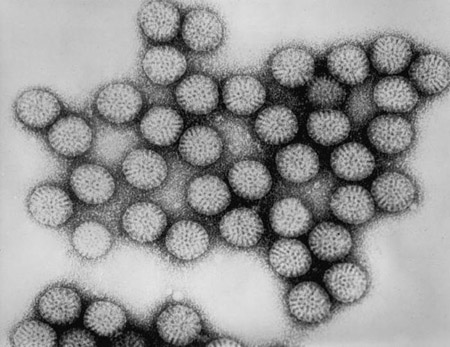
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- რისკ-ფაქტორების არსებობა
- 5 წლამდე ასაკი
- ექსპოზიცია გასტროენტერიტის მქონე პირებზე
- აუცრელობა როტავირუსის წინააღმდეგ
- პირღებინება
- უსისხლო დიარეა
- ნაწლავის მომატებული ხმიანობა
Other diagnostic factors
- მუცლის ტკივილი
- სუბფებრილური ცხელება
- დეჰიდრატაციის მტკიცებულება
- წონის კლება
- მუცელი გადაბერილი არ არის
- მუცლის ტკივილი
- ლორწო განავალში
Risk factors
- 5 წლამდე ასაკი
- ცუდი პირადი ჰიგიენა
- ექსპოზიცია გასტროენტერიტის მქონე პირებზე
- საბავშვო ბაღები
- ზამთრის თვეები
- სიღარიბე
- აუცრელობა როტავირუსის წინააღმდეგ
- ძუძუთი კვების ნაკლებობა
- იმუნოდეფიციტი
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- კლინიკური გასინჯვა
Investigations to consider
- შრატში ელექტროლიტები, შარდოვანა და კრეატინინი
- FBC
- სისხლის კულტურები
- განავლის მიკროსკოპია
- განავლის ბაქტერიოლოგიური ანალიზი
- იმუნოფერმენტული ანალიზი (EIA) ვირუსული ანტიგენის აღმოსაჩენად
- განავლის ელექტრონული მიკროსკოპია
Treatment algorithm
დეჰიდრატაციის გარეშე
მსუბუქი დეჰიდრატაცია (<5%)
საშუალო დეჰიდრატაცია (5% to 10%)
მძიმე დეჰიდრატაცია (>10%)
Contributors
Authors
Alexander K.C. Leung, MB BS, FRCPC, FRCP, FRCPCH, FAAP

Clinical Professor of Pediatrics
The University of Calgary
Calgary
Alberta
Canada
Disclosures
AKCL is an author of a guideline and a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Saul Greenberg, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Paediatrics
University of Toronto
Ontario
Canada
Disclosures
SG declares that he has no competing interests.
Y.L. Lau, MBCBhB, MD, FRCP, FRCPCH, FRCPS, FHKAM, FHKCPaed
Professor
Faculty of Medicine
University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Disclosures
YLL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Leung AK, Kellner JD, Davies HD. Rotavirus gastroenteritis. Adv Ther. 2005 Sep-Oct;22(5):476-87. Abstract
Cortese MM, Parashar UD; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis among infants and children: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2009 Feb 6;58(RR-2):1-25.Full text Abstract
Le Saux N; Canadian Pediatric Society. Position statement: recommendations for the use of rotavirus vaccines in infants. Oct 2018 [internet publication].Full text
Leung A, Prince T; Canadian Paediatric Society. Oral rehydration therapy and early refeeding in the management of childhood gastroenteritis. Paediatr Child Health. 2006 Nov;11(8):527-31.Full text
Carter B, Fedorowicz Z. Antiemetic treatment for acute gastroenteritis in children: an updated Cochrane systematic review with meta-analysis and mixed treatment comparison in a Bayesian framework. BMJ Open. 2012 Jul 19;2(4):e000622.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer