Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- რისკ-ფაქტორების არსებობა
- სიყვითლე
- არასპეციფიკური ტკივილი ან დისკომფორტი მუცლის ზედა არეში
- წონაში კლება და მადის დაქვეითება (ანორექსია)
- წელის ტკივილი
Other diagnostic factors
- 65-75 წლის ასაკში
- სტეატორეა
- წყურვილი, პოლიურია, ნიქტურია და წონის კლება
- გულისრევა, ღებინება და ადრეული გაჯერება
- აუხსნელი მწვავე პანკრეატიტი
- ჰეპატომეგალია.
- წარმონაქმნი ეპიგასტრიუმში
- დადებითია კურვაზიეს ნიშანი
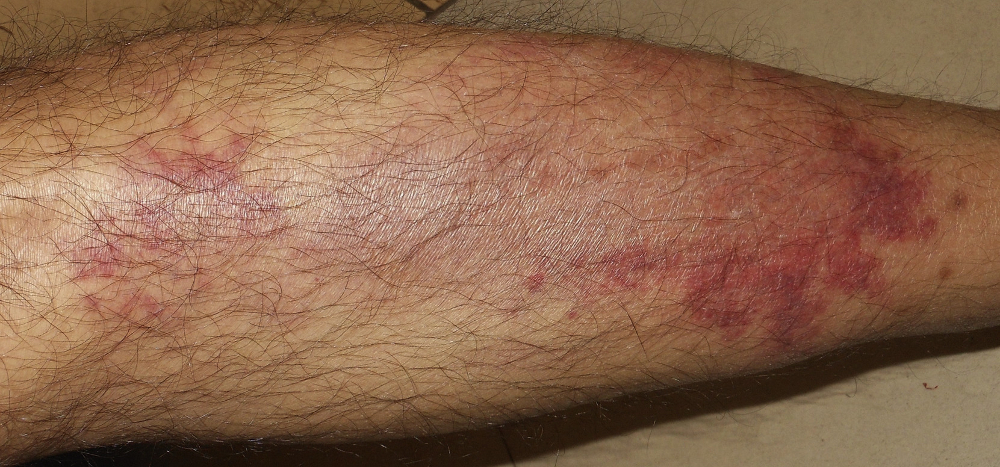
- პეტექიები, პურპურა, სისხლნაჟღენთები
- ტრუსოს ნიშანი (მიგრაციული თრომბოფლებიტი)
Risk factors
- მოწევა
- პანკრეასის კიბოს ოჯახური ანამნეზი
- კიბოს სხვა მემკვიდრული სინდრომები
- ქრონიკული სპორადული პანკრეატიტი
- შაქრიანი დიაბეტი
- სიმსუქნე
- კვებითი ფაქტორები
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- კომპიუტერული ტომოგრაფია პანკრეასის პროტოკოლით
- მუცლის ღრუს ულტრაბგერითი გამოკვლევა
- LFT
Investigations to consider
- პროთრომბინის დრო (PT)
- FBC
- ბიომარკერი - კიბოს ანტიგენი 19-9
- პოზიტრონულ-ემისიური ტომოგრაფია (PET)
- ენდოსკოპიური რეტროგრადული ქოლანგიოპანკრეატოგრაფია (ERCP)
- მუცლის ღრუს მაგნიტურ-რეზონანსული ტომოგრაფია
- მაგნიტურ-რეზონანსული ქოლანგიოპანკრეატოგრაფია
- ენდოსკოპიური ულტრაბგერა
- ლაპარასკოპია სტადიის განსაზღვრის მიზნით (ულტრაბგერით)
- ბიოფსიის
Emerging tests
- გენომის ტესტირება
Treatment algorithm
რეზექტაბელური დაავადება (1-ლი და მე-2 სტადია)
ადგილობრივად გავრცელებული არარეზექტაბელური დაავადება (მე-3 სტადია)
მეტასტაზური დაავადება (მე-4 სტადია)
Contributors
Authors
Hemant M. Kocher, MBBS, MS, MD, FRCS
Professor of Liver and Pancreas Surgery
Barts Cancer Institute
Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry
London
UK
Disclosures
HMK is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. HMK has received trial funding from Celgene and Bristol-Myers Squibb, advisory board honorarium from Baxalta Inc., and educational grants from Mylan, Celgene, Ethicon, and Medtronic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Hemant M. Kocher wishes to gratefully acknowledge Dr Fieke E.M. Froeling, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
FEMF is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Ross Carter, FRCS
Consultant Pancreatic Surgeon
West of Scotland Pancreatic Unit
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
Not disclosed.
Nikhil I. Khushalani, MD
Assistant Professor of Oncology
Roswell Park Cancer Institute
Buffalo
NY
Disclosures
NIK has received funding for the conduction of clinical trials and associated translational studies from Merck, Pfizer, and Astra-Zeneca. NIK has a grant from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (from research support by Roche).
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: pancreatic adenocarcinoma [internet publication].Full text
Sohal DPS, Kennedy EB, Cinar P, et al. Metastatic pancreatic cancer: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug 5:JCO2001364.Full text Abstract
Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med. 2013 Oct 31;369(18):1691-703.Full text Abstract
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011 May 12;364(19):1817-25.Full text Abstract
Balaban EP, Mangu PB, Khorana AA, et al. Locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug 1;34(22):2654-68.Full text Abstract
Ducreux M, Cuhna AS, Caramella C, et al. Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015 Sep;26(5 suppl):v56-68.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- ქრონიკული პანკრეატიტი
- კენჭები სანაღვლე სადინარში
- ამპულური ნაწილის კარცინომა
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic cancer
- Clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic cancer
More GuidelinesPatient information
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreas cancer: questions to ask your doctor
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer