შეჯამება
განსაზღვრება
ანამნეზი და გასინჯვა
ძირითადი დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- რისკ-ფაქტორების არსებობა
- დიარეა
- მუცლის ტკივილი
სხვა დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- ცხელება
- მუცლის ტკივილი
- გულისრევა და ღებინება
- მუცლის შებერვა
- შოკის სიმპტომები
რისკფაქტორები
- ანტიბიოტიკების გავლენა
- ხანდაზმული ასაკი
- ჰოსპიტალიზაცია ან მოხუცთა თავშესაფარში ცხოვრება
- ოჯახის ინფიცირებულ წევრთან ექსპოზიცია
- - Clostridium difficile-თან დაკავშირებული დაავადების ანამნეზი
- მჟავიანობის დამაქვეითებელი პრეპარატების გამოყენება
- ნაწლავთა ანთებითი დაავადება
- პაციენტები, რომელთაც ჩაუტარდათ მყარი ორგანოების ტრანსპლანტაცია
- ჰემატოპოეზური ღეროვანი უჯრედების ტრანსპლანტის რეციპიენტები
- თირკმლის ქრონიკული დაავადება
- HIV ინფექცია
- იმუნოსუპრესიული მედიკამენტები ან ქიმიოთერაპია
- კუჭ-ნაწლავის ქირურგია
- D ვიტამინის ნაკლებობა
დიაგნოსტიკური კვლევები
1-ად შესაკვეთი გამოკვლევები
- FBC
- განავლის გვაიაკური სინჯი (განავლის ანალიზი ფარულ სისხლდენაზე)
- განავლის პოლიმერაზული ჯაჭვური რეაქცია (PCR)
- განავლის იმუნოლოგიური ანალიზი გლუტამატ დეჰიდროგენაზაზე
- განავლის იმუნოლოგიური ანალიზი A და B ტოქსინებზე
- მუცლის ღრუს რენტგენოგრაფია
გასათვალისწინებელი კვლევები
- უჯრედული კულტურის ციტოტოქსიკურობის ნეიტრალიზაციის ანალიზი
- მუცლის კომპიუტერული ტომოგრაფიით
- სიგმოიდისკოპია ან კოლონოსკოპია
ახალი ტესტები
- განავლის ლაქტოფერინი ან კალპროტექტინი
მკურნალობის ალგორითმი
საწყისი ეპიზოდი: არა მძიმე
საწყისი ეპიზოდი: მძიმე
საწყისი ეპიზოდი: ელვისებრი
პირველი რეციდივი
შემდგომი რეციდივი
კონტრიბუტორები
ავტორები
Ali Hassoun, MD, FACP, FIDSA, AAHIVS
Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Alabama Infectious Diseases Center
Huntsville
AL
გაფრთხილება:
AH declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტები
Julius Atashili, MD, MPH
Department of Epidemiology
Division of General Medicine and Epidemiology
UNC at Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill
NC
გაფრთხილება:
JA declares that he has no competing interests.
Satish Keshav, MBBCh, DPhil, FRCP
Consultant Gastroenterologist
Department of Gastroenterology
John Radcliffe Hospital
Oxford
UK
გაფრთხილება:
SK declares that he has no competing interests.
Ian Beales, MD, FRCP
Clinical Reader and Consultant Gastroenterologist
Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital
Norwich
UK
გაფრთხილება:
IB declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტების განცხადებები
BMJ Best Practice-ის თემების განახლება სხვადასხვა პერიოდულობით ხდება მტკიცებულებებისა და რეკომენდაციების განვითარების შესაბამისად. ქვემოთ ჩამოთვლილმა რეცენზენტებმა თემის არსებობის მანძილზე კონტენტს ერთხელ მაინც გადახედეს.
გაფრთხილება
რეცენზენტების აფილიაციები და გაფრთხილებები მოცემულია გადახედვის მომენტისთვის.
წყაროები
ძირითადი სტატიები
McDonald LC, Gerding DN, Johnson S, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Mar 19;66(7):e1-e48.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Johnson S, Lavergne V, Skinner AM, et al. Clinical practice guideline by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 focused update guidelines on management of Clostridioides difficile infection in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 24:ciab549.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
van Prehn J, Reigadas E, Vogelzang EH, et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: 2021 update on the treatment guidance document for Clostridioides difficile infection in adults. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Dec;27 Suppl 2:S1-S21.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Beinortas T, Burr NE, Wilcox MH, et al. Comparative efficacy of treatments for Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018 Sep;18(9):1035-44. აბსტრაქტი
Nelson RL, Suda KJ, Evans CT. Antibiotic treatment for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;(3):CD004610.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
გამოყენებული სტატიები
ამ თემაში მოხსენიებული წყაროების სრული სია ხელმისაწვდომია მომხმარებლებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ წვდომა BMJ Best Practice-ის ყველა ნაწილზე.
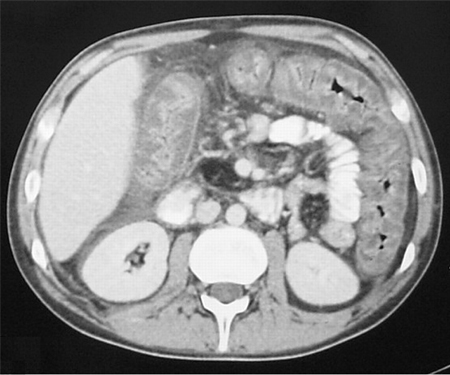
დიფერენციული დიაგნოზები
- ანტიბიოტიკებით გამოწვეული დიარეა (AAD)
- იშემიური კოლიტი
- ბაქტერიული ან ვირუსული გასტროენტერიტი
მეტი დიფერენციული დიაგნოზებიგაიდლაინები
- Japanese clinical practice guidelines for management of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile infection
- Management of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in hematopoietic cell transplant patients
მეტი გაიდლაინებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას