შეჯამება
განსაზღვრება
ანამნეზი და გასინჯვა
ძირითადი დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- აივ-დადებითი
სხვა დიაგნოსტიკური ფაქტორები
- პირ-ხახის კანდიდოზი
- განმეორებითი ბაქტერიული პნევმონია
- წონაში კლება
- სიმპტომების უფრო მეტი ხანგრძლივობა (აივ-დადებითი პაციენტები)
- სიმპტომების სწრაფი დაწყება (აივ-უარყოფითი პაციენტები)
- ცხელება
- მშრალი ხველა
- ქოშინი
- დაღლილობა
- გულ-მკერდის გამოკვლევის შედეგები ნორმაშია
- ტაქიკარდია
- ტაქიპნოე ან რესპირატორული დისტრესი
- ციანოზი
- ფილტვგარე გამოვლინებები
- გულმკერდი პლევრიტული ტკივილიგულმკერდის პლევრიტული ტკივილი
- ცალმხრივად დაქვეითებული სუნთქვითი ხმიანობა
რისკფაქტორები
- CD4 უჯრედების 200 უჯრედი/მიკროლიტრ-ზე ნაკლები რაოდენობა
- იმუნოკომპრომისული მდგომარეობა
- ქრონიკული კორტიკოსტეროიდული მკურნალობა
- გადატანილი პნევმოცისტური პნევმონია
დიაგნოსტიკური კვლევები
1-ად შესაკვეთი გამოკვლევები
- გულმკერდის რენტგენი
- არტერიული სისხლის აირები
- LDH-ის დონე შრატში
- ინდუცირებული ნახველის
გასათვალისწინებელი კვლევები
- გულ-მკერდის მაღალი რეზოლუციის კომპიუტერული ტომოგრაფია (HRCT)
- სუნთქვის ფუნქციური სინჯები
- ბრონქოსკოპია და ბრონქოალველოური ლავაჟი (BAL)
- ბიოფსიის
ახალი ტესტები
- პოლიმერაზული ჯაჭვური რეაქცია (PCR)
- პლაზმაში S-ადენოზილმეთიონინის დონე
- შრატის (1,3)-ბეტა-D-გლუკანის დონე
მკურნალობის ალგორითმი
პნევმოცისტური პნევმონიის მაღალი რისკი
მოზრდილები ან მოზარდები: აივ-დადებითი
ბავშვები: აივ-დადებითი ან აივ რისკის ქვეშ მყოფი
იმუნოკომპრომისული ზრდასრულები ან მოზარდები: აივ უარყოფითი და ტრანსპლანტაციის ანამნეზის გარეშე
იმუნოკომპრომისული ზრდასრულები ან მოზარდები ან ბავშვები: აივ-უარყოფითი, ტრანსპლანტაციის მიმღები პაციენტები
ჩაუტარდა PCP ინფექციის წარმატებული მკურნალობაა
კონტრიბუტორები
ავტორები
Alison Morris, MD, MS

Professor of Medicine
Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
გაფრთხილება:
AM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Ioannis Konstantinidis, MD, MS
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
PA
გაფრთხილება:
IK declares that he has no competing interests.
მადლიერება
Dr Alison Morris and Dr Ioannis Konstantinidis would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Eric Nolley and Dr Matthew Gingo, previous contributors to this topic.
გაფრთხილება:
EN and MG declare that they have no competing interests.
რეცენზენტები
Peter D. Walzer, MD, MSc
Associate Chief of Staff for Research
Cincinnati VA Medical Center
Professor of Medicine
University of Cincinnati
Cincinnati
OH
გაფრთხილება:
PDW declares that he has no competing interests.
David Spencer, MBChB(UCT), MMed (Wits)
Specialist Physician and Consultant
Toga Laboratory and Kimera Consultants
Edenvale
Johannesburg
South Africa
გაფრთხილება:
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Graeme Meintjes, MBChB, MRCP, FCP, DipHIVMan
Infectious Diseases Physician
Institute of Infectious Diseases and Molecular Medicine
Faculty of Health Sciences
University of Cape Town
Observatory
South Africa
გაფრთხილება:
GM declares that he has no competing interests.
რეცენზენტების განცხადებები
BMJ Best Practice-ის თემების განახლება სხვადასხვა პერიოდულობით ხდება მტკიცებულებებისა და რეკომენდაციების განვითარების შესაბამისად. ქვემოთ ჩამოთვლილმა რეცენზენტებმა თემის არსებობის მანძილზე კონტენტს ერთხელ მაინც გადახედეს.
გაფრთხილება
რეცენზენტების აფილიაციები და გაფრთხილებები მოცემულია გადახედვის მომენტისთვის.
წყაროები
ძირითადი სტატიები
Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman FC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1998 Mar 26;338(13):853-60.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
National Institutes of Health; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America; Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society; American Academy of Pediatrics. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in childrenwith and exposed to HIV: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. 2013 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Institutes of Health; HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in adults and adolescents with HIV. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Mar 2019 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
Taplitz RA, Kennedy EB, Bow EJ, et al. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for adult patients with cancer-related immunosuppression: ASCO and IDSA clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018 Oct 20;36(30):3043-54.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009 Oct;15(10):1143-238.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Fishman JA, Gans H, AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Pneumocystis jiroveci in solid organ transplantation: guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. 2019 Sep;33(9):e13587. აბსტრაქტი
Limper AH, Knox KS, Sarosi GA, et al. An official American Thoracic Society statement: treatment of fungal infections in adult pulmonary and critical care patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Jan 1;183(1):96-128.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Ewald H, Raatz H, Boscacci R, et al. Adjunctive corticosteroids for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 2;(4):CD006150.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Cooley L, Dendle C, Wolf J, et al. Consensus guidelines for diagnosis, prophylaxis and management of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological and solid malignancies, 2014. Intern Med J. 2014 Dec;44(12b):1350-63.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Maertens J, Cesaro S, Maschmeyer G, et al. ECIL guidelines for preventing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Sep;71(9):2397-404.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
Classen AY, Henze L, von Lilienfeld-Toal M, et al. Primary prophylaxis of bacterial infections and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with hematologic malignancies and solid tumors: 2020 updated guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (AGIHO/DGHO). Ann Hematol. 2021 Jun;100(6):1603-1620.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
გამოყენებული სტატიები
ამ თემაში მოხსენიებული წყაროების სრული სია ხელმისაწვდომია მომხმარებლებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ წვდომა BMJ Best Practice-ის ყველა ნაწილზე.
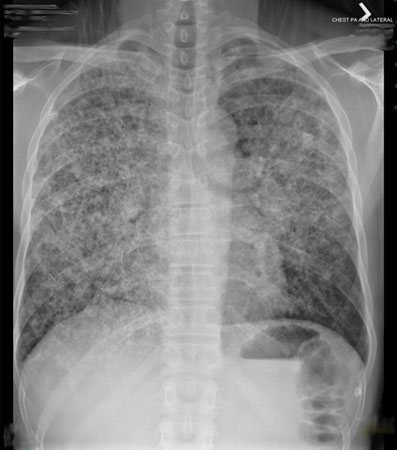
დიფერენციული დიაგნოზები
- 2019 წლის კორონავირუსით გამოწვეული დაავადება (COVID-19)
- ბაქტერიული პნევმონია
- კოკციდიოიდომიკოზი
მეტი დიფერენციული დიაგნოზებიგაიდლაინები
- Primary prophylaxis of bacterial infections and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with hematologic malignancies and solid tumors
- Pneumocystis jiroveci in solid organ transplantation
მეტი გაიდლაინებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას